Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC): rationale, development, and implementation
- PMID: 30269452
- PMCID: PMC6166039
- DOI: 10.15441/ceem.17.259
Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC): rationale, development, and implementation
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to describe the conceptualization, development, and implementation processes of the newly established Korean Cardiac Arrest Resuscitation Consortium (KoCARC) to improve out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) outcomes.
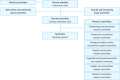
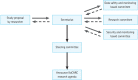
Methods: The KoCARC was established in 2014 by recruiting hospitals willing to participate voluntarily. To enhance professionalism in research, seven research committees, the Epidemiology and Preventive Research Committee, Community Resuscitation Research Committee, Emergency Medical System Resuscitation Research Committee, Hospital Resuscitation Research Committee, Hypothermia and Postresuscitation Care Research Committee, Cardiac Care Resuscitation Committee, and Pediatric Resuscitation Research Committee, were organized under a steering committee. The KoCARC registry was developed with variables incorporated in the currently existing regional OHCA registries and Utstein templates and were collected via a web-based electronic database system. The KoCARC study population comprises patients visiting the participating hospitals who had been treated by the emergency medical system for OHCA presumed to have a cardiac etiology.
Results: A total of 62 hospitals volunteered to participate in the KoCARC, which captures 33.0% of the study population in Korea. Web-based data collection started in October 2015, and to date (December 2016), there were 3,187 cases compiled in the registry collected from 32 hospitals.
Conclusion: The KoCARC is a self-funded, voluntary, hospital-based collaborative research network providing high level evidence in the field of OHCA and resuscitation. This paper will serve as a reference for subsequent KoCARC manuscripts and for data elements collected in the study.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest; Research.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Berdowski J, Berg RA, Tijssen JG, Koster RW. Global incidences of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and survival rates: systematic review of 67 prospective studies. Resuscitation. 2010;81:1479–87. - PubMed
-
- Ro YS, Shin SD, Song KJ, et al. A trend in epidemiology and outcomes of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest by urbanization level: a nationwide observational study from 2006 to 2010 in South Korea. Resuscitation. 2013;84:547–57. - PubMed
-
- Herlitz J, Ekstrom L, Wennerblom B, Axelsson A, Bang A, Holmberg S. Prognosis among survivors of prehospital cardiac arrest. Ann Emerg Med. 1995;25:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Stiell IG, Wells GA, DeMaio VJ, et al. Modifiable factors associated with improved cardiac arrest survival in a multicenter basic life support/defibrillation system: OPALS Study Phase I results. Ontario Prehospital Advanced Life Support. Ann Emerg Med. 1999;33:44–50. - PubMed
-
- Ong ME, Shin SD, Tanaka H, et al. Pan-Asian Resuscitation Outcomes Study (PAROS): rationale, methodology, and implementation. Acad Emerg Med. 2011;18:890–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources