Regulation of RIP3 protein stability by PELI1-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation
- PMID: 30269743
- PMCID: PMC6235095
- DOI: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.10.217
Regulation of RIP3 protein stability by PELI1-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation
Abstract
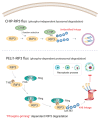
Receptor-interacting protein kinase-3 (RIP3 or RIPK3) is a serine-threonine kinase largely essential for necroptotic cell death; it also plays a role in some inflammatory diseases. High levels of RIP3 are likely sufficient to activate necroptotic and inflammatory pathways downstream of RIP3 in the absence of an upstream stimulus. For example, we have previously detected high levels or RIP3 in the skin of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis patients; this correlates with increased phosphorylation of MLKL found in these patients. We have long surmised that there are molecular mechanisms to prevent anomalous activity of the RIP3 protein, and so prevent undesirable cell death and inflammatory effects when inappropriately activated. Recent discovery that Carboxyl terminus of Hsp 70-Interacting Protein (CHIP) could mediate ubiquitylation- and lysosomedependent RIP3 degradation provides a potential protein that has this capacity. However, while screening for RIP3-binding proteins, we discovered that pellino E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 (PELI1) also interacts directly with RIP3 protein; further investigation in this study revealed that PELI1 also targets RIP3 for proteasome-dependent degradation. Interestingly, unlike CHIP, which targets RIP3 more generally, PELI1 preferentially targets kinase active RIP3 that has been phosphorylated on T182, subsequently leading to RIP3 degradation. [BMB Reports 2018; 51(10): 484-485].
Figures
Similar articles
-
PELI1 Selectively Targets Kinase-Active RIP3 for Ubiquitylation-Dependent Proteasomal Degradation.Mol Cell. 2018 Jun 7;70(5):920-935.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.016. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29883609
-
E3 ligase TRIM25 ubiquitinates RIP3 to inhibit TNF induced cell necrosis.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Oct;28(10):2888-2899. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00790-3. Epub 2021 May 5. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33953350 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulated RIP3 Expression Potentiates MLKL Phosphorylation-Mediated Programmed Necrosis in Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis.J Invest Dermatol. 2015 Aug;135(8):2021-2030. doi: 10.1038/jid.2015.90. Epub 2015 Mar 6. J Invest Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25748555
-
More to life than death: molecular determinants of necroptotic and non-necroptotic RIP3 kinase signaling.Curr Opin Immunol. 2014 Feb;26:76-89. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.10.017. Epub 2013 Nov 30. Curr Opin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24556404 Review.
-
The serine threonine kinase RIP3: lost and found.BMB Rep. 2015 Jun;48(6):303-12. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.6.068. BMB Rep. 2015. PMID: 25858093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein phosphatases in TLR signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Apr 21;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00722-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33882943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biology of Pellino1: a potential therapeutic target for inflammation in diseases and cancers.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 18;14:1292022. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1292022. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38179042 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

