Structural Remodeling of the Human Colonic Mesenchyme in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- PMID: 30270042
- PMCID: PMC6176871
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.067
Structural Remodeling of the Human Colonic Mesenchyme in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
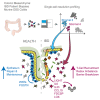
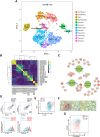
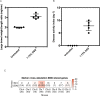
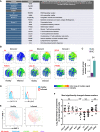
Intestinal mesenchymal cells play essential roles in epithelial homeostasis, matrix remodeling, immunity, and inflammation. But the extent of heterogeneity within the colonic mesenchyme in these processes remains unknown. Using unbiased single-cell profiling of over 16,500 colonic mesenchymal cells, we reveal four subsets of fibroblasts expressing divergent transcriptional regulators and functional pathways, in addition to pericytes and myofibroblasts. We identified a niche population located in proximity to epithelial crypts expressing SOX6, F3 (CD142), and WNT genes essential for colonic epithelial stem cell function. In colitis, we observed dysregulation of this niche and emergence of an activated mesenchymal population. This subset expressed TNF superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), fibroblastic reticular cell-associated genes, IL-33, and Lysyl oxidases. Further, it induced factors that impaired epithelial proliferation and maturation and contributed to oxidative stress and disease severity in vivo. Our work defines how the colonic mesenchyme remodels to fuel inflammation and barrier dysfunction in IBD.
Keywords: CyTOF; SOX6; TNFSF14; Wnts; crypt niche; inflammatory bowel disease; mesenchyme; single-cell RNA-seq; stratification; stromal cell; target discovery.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures









References
-
- Angerer P., Haghverdi L., Büttner M., Theis F.J., Marr C., Buettner F. destiny: Diffusion maps for large-scale single-cell data in R. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:1241–1243. - PubMed
-
- Bao S., Ouyang G., Bai X., Huang Z., Ma C., Liu M., Shao R., Anderson R.M., Rich J.N., Wang X.F. Periostin potently promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell. 2004;5:329–339. - PubMed
-
- Barker N. Adult intestinal stem cells: Critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014;15:19–33. - PubMed
-
- Bernardo M.E., Fibbe W.E. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13:392–402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

