The role of hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers in the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 30271115
- PMCID: PMC6151102
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S175887
The role of hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers in the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to analyze the effects of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) stabilizers on anemia in non-dialysis-dependent (NDD) and dialysis-dependent (DD) chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients.
Methods: Published studies were extracted from PubMed, China Biological Medicine Database (CBM), Wanfang database, and Cochrane Library on March 10, 2018, and relevant studies were pooled and included in a meta-analysis. Data on hemoglobin (Hb), ferritin, and hepcidin levels, total iron-binding capacity (TIBC), and incidence of adverse events (AEs) were extracted and pooled using Review Manager Version 5.3.
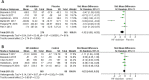
Results: Data from nine selected studies were extracted. Meta-analysis of the included studies showed that HIF stabilizers reduced ferritin and hepcidin levels and increased Hb level and TIBC in NDD-CKD patients. However, HIF stabilizers only increased TIBC, and did not affect ferritin, hepcidin, and Hb levels in DD-CKD patients. Furthermore, no notable differences in AEs and severe AEs between NDD-CKD and DD-CKD patients were detected.
Conclusion: HIF stabilizers are effective for the treatment of anemia in NDD-CKD patients and safe for short-term use.
Keywords: anemia; chronic kidney disease; hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizer; meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Lew QLJ, Allen JC, Nguyen F, Tan NC, Jafar TH. Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease and Their Clinical Utility in Primary Care Clinics in a Multi-Ethnic Southeast Asian Population. Nephron. 2018;138(3):202–213. - PubMed
-
- del Vecchio L, Locatelli F. Roxadustat in the treatment of anaemia in chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2018;27(1):125–133. - PubMed
-
- Riley MV, Vess J, Dumas BP. Home Therapy to Reduce Office Visits for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Anemia. Nephrol Nurs J. 2017;44(1):29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

