Inhibition of NKCC1 Modulates Alveolar Fluid Clearance and Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Lung Injury via TRAF6-Mediated Pathways
- PMID: 30271405
- PMCID: PMC6146090
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02049
Inhibition of NKCC1 Modulates Alveolar Fluid Clearance and Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion Lung Injury via TRAF6-Mediated Pathways
Abstract
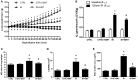
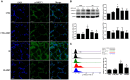
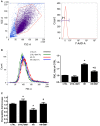
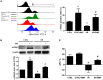
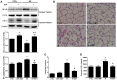
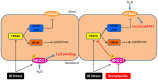
Background: The expression of Na-K-2Cl cotransporter 1 (NKCC1) in the alveolar epithelium is responsible for fluid homeostasis in acute lung injury (ALI). Increasing evidence suggests that NKCC1 is associated with inflammation in ALI. We hypothesized that inhibiting NKCC1 would attenuate ALI after ischemia-reperfusion (IR) by modulating pathways that are mediated by tumor necrosis-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). Methods: IR-ALI was induced by producing 30 min of ischemia followed by 90 min of reperfusion in situ in an isolated and perfused rat lung model. The rats were randomly allotted into four groups comprising two control groups and two IR groups with and without bumetanide. Alveolar fluid clearance (AFC) was measured for each group. Mouse alveolar MLE-12 cells were cultured in control and hypoxia-reoxygenation (HR) conditions with or without bumetanide. Flow cytometry and transwell monolayer permeability assay were carried out for each group. Results: Bumetanide attenuated the activation of p-NKCC1 and lung edema after IR. In the HR model, bumetanide decreased the cellular volume and increased the transwell permeability. In contrast, bumetanide increased the expression of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), which attenuated the reduction of AFC after IR. Bumetanide also modulated lung inflammation via nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). TRAF6, which is upstream of p38 MAPK and NF-κB, was attenuated by bumetanide after IR and HR. Conclusions: Inhibition of NKCC1 by bumetanide reciprocally modulated epithelial p38 MAPK and NF-κB via TRAF6 in IR-ALI. This interaction attenuated the reduction of AFC via upregulating ENaC expression and reduced lung inflammation.
Keywords: Na-K-2Cl cotransporter 1; acute lung injury; alveolar fluid clearance; bumetanide; epithelial sodium channel; ischemia-reperfusion; p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; tumor necrosis-associated factor 6.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Acute Hyperglycemia Aggravates Lung Injury via Activation of the SGK1-NKCC1 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 7;21(13):4803. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134803. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32645929 Free PMC article.
-
Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 18;14(7):e0219788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219788. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31318922 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Na-K-Cl cotransporter isoform 1 reduces lung injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 Jan;153(1):206-215. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2016.09.068. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 27986254
-
The roles of sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter isoform-1 in acute lung injury.Tzu Chi Med J. 2021 Jul 5;34(2):119-124. doi: 10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_50_21. eCollection 2022 Apr-Jun. Tzu Chi Med J. 2021. PMID: 35465284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CNS pharmacology of NKCC1 inhibitors.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Mar 1;205:108910. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2021.108910. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 34883135 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathways in the Pathophysiology of Coronavirus 19 Lung Disease Accessible to Prevention and Treatment.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 14;11:872. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00872. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32922301 Free PMC article.
-
Pellino1 promoted inflammation in lung injury model of sepsis by TRAF6/ NF-κB signal pathway.J Inflamm (Lond). 2021 Feb 25;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12950-021-00276-6. J Inflamm (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33632252 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Plastrum Testudinis Extracts on the Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of rBMSCs by Regulating p38 MAPK-Related Genes.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Mar 7;2019:6815620. doi: 10.1155/2019/6815620. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30984279 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-146a overexpression alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury in mice.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Sep;22(3):937. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10369. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34335886 Free PMC article.
-
SPAK-p38 MAPK signal pathway modulates claudin-18 and barrier function of alveolar epithelium after hyperoxic exposure.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Feb 15;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01408-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 33588817 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

