Engineering a customized nanodrug delivery system at the cellular level for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 30271427
- PMCID: PMC6157601
- DOI: 10.1007/s11426-017-9176-3
Engineering a customized nanodrug delivery system at the cellular level for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
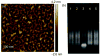
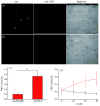
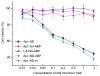
Drug administration customized to individual cells could intrinsically address cancer heterogeneity and provide a safe and effective method for delivering personalized treatment. To accomplish this, we developed a smart nanodrug delivery system characterized by cancer cell-targeted drug delivery and intracellular biomarker-responsive drug activation. This system was composed of a long-nicked DNA duplex formed by tandem hybridization of two extended antisense oligonucleotides whose ends were separately blocked with a cancer cell-specific aptamer, AS1411, and a replaceable anti-biomarker probe (ABP). We demonstrated that this DNA nanodrug was directed to cancer cells with the guidance power of AS1411 and then activated by the presence of a given intracellular biomarker. By using such a belt-and-braces strategy, this DNA nanodrug system could safely and efficiently accelerate apoptosis of target cancer cells. Moreover, since the expression level of biomarkers tends to indicate the specific physiological state of individual cells, biomarker-responsive activation of the nanodrug is expected to enable customized drug administration at the cellular level.
Keywords: antisense oligonucleotides; aptamer; drug delivery; personalized medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A cell-targeted, size-photocontrollable, nuclear-uptake nanodrug delivery system for drug-resistant cancer therapy.Nano Lett. 2015 Jan 14;15(1):457-63. doi: 10.1021/nl503777s. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Nano Lett. 2015. PMID: 25479133 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Aptamer Chimera for Targeted Delivery and ATP-Responsive Release of Doxorubicin into Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12940. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312940. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884745 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Functionalized and Backbone Redox-Responsive Hyperbranched Polymer for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy.Biomacromolecules. 2016 Jun 13;17(6):2050-62. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00262. Epub 2016 May 4. Biomacromolecules. 2016. PMID: 27113017
-
[Research Progress on the Influence of Tumor Extracellular Matrix Mechanic Properties on Nanodrug Delivery].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jan 20;55(1):13-18. doi: 10.12182/20240160205. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38322528 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Recent advances of nanodrug delivery system in the treatment of hematologic malignancies.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 2):607-623. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.03.016. Epub 2022 Mar 23. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35339668 Review.
Cited by
-
Aptamer-engineered (nano)materials for theranostic applications.Theranostics. 2023 Sep 25;13(15):5183-5206. doi: 10.7150/thno.85419. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37908725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Layer-by-Layer Multitargeting Strategy for Enhanced Photothermal Therapy.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 8;10(6):5460-5467. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07611. eCollection 2025 Feb 18. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39989810 Free PMC article.
-
Stretchable Full-Color Phosphorescent PVA-Based Ionogels for Multimodal Sensing-Visual Integration Applications.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Feb;12(5):e2411229. doi: 10.1002/advs.202411229. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39665311 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing biomedicine: Aptamer-based nanomaterials and nanodevices for therapeutic applications.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024 May 24;42:e00843. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00843. eCollection 2024 Jun. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38881649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aptamer-ODN Chimeras: Enabling Cell-Specific ODN Targeting Therapy.Cells. 2025 May 12;14(10):697. doi: 10.3390/cells14100697. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40422200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berger MF, Lawrence MS, Demichelis F, Drier Y, Cibulskis K, Si-vachenko AY, Sboner A, Esgueva R, Pflueger D, Sougnez C, Onofrio R, Carter SL, Park K, Habegger L, Ambrogio L, Fennell T, Parkin M, Saksena G, Voet D, Ramos AH, Pugh TJ, Wilkinson J, Fisher S, Winckler W, Mahan S, Ardlie K, Baldwin J, Simons JW, Kitabayashi N, MacDonald TY, Kantoff PW, Chin L, Gabriel SB, Gerstein MB, Golub TR, Meyerson M, Tewari A, Lander ES, Getz G, Rubin MA, Garraway LA. Nature. 2011;470:214–220. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sander C. Science. 2000;287:1977–1978. - PubMed
-
- Almendro V, Marusyk A, Polyak K. Annu Rev Pathol Mech Dis. 2013;8:277–302. - PubMed
-
- Niidome T, Huang L. Gene Ther. 2002;9:1647–1652. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
