Prognostic value of Systemic immune-inflammation index in cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30271489
- PMCID: PMC6160683
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.25691
Prognostic value of Systemic immune-inflammation index in cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), on the basis of lymphocyte, neutrophil and platelet counts had been published to be a good prognostic factor in multiple cancers. Nevertheless, the prognostic value of SII in cancer patients remains inconsistent. Therefore, we carried out a meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic value of SII in these patients with cancer. A total of 22 articles with 7657 patients enrolled in this meta-analysis. The combined result revealed that a high SII was evidently correlated with poor overall survival (OS) (HR=1.69, 95%CI=1.42-2.01, p<0.001), poor time to recurrent (TTR) (HR=1.87, p<0.001) , poor progress-free survival (PFS) (HR=1.61, p=0.012) ,poor cancer-specific survival (CSS) (HR=1.44, p=0.027) , poor relapse-free survival (RFS) (HR=1.66, p=0.025) and poor disease-free survival (DFS) (HR=2.70, p<0.001) in patients with cancers. Subgroup analysis indicated that SII over the cutoff value could predict worse overall survival in Hepatocellular carcinoma (p<0.001), Gastric cancer (p=0.005), Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (p=0.013), Urinary system cancer (p<0.001), Small cell lung cancer (p<0.001), Non-Small cell lung cancer (p<0.001) and Acral Melanoma (p<0.001). The largest effect size was observed in the Hepatocellular carcinoma (HR=2.11). In addition, these associations did not vary significantly by the cutoff value, sample size and ethnicity. Therefore, high SII may be a potential prognostic marker in patients with various cancers and associated with the poor overall outcomes.
Keywords: Systemic immune-inflammation index; cancer; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
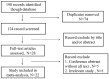

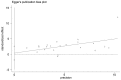
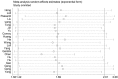
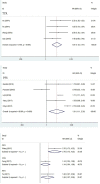
Similar articles
-
The Value of the Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Predicting Survival Outcomes in Patients with Brain Metastases of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Stereotactic Radiotherapy.Mediators Inflamm. 2021 Oct 29;2021:2910892. doi: 10.1155/2021/2910892. eCollection 2021. Mediators Inflamm. 2021. PMID: 34744510 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with urinary system cancers: a meta-analysis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1302-1310. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24834. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629300
-
Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2022 Nov;22(4):637-646. doi: 10.1007/s10238-021-00785-x. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Clin Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35022918
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index is a promising non-invasive biomarker for predicting the survival of urinary system cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):1827-1838. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1991591. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 34647517 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in surgical esophageal cancer patients: An updated meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2022 Aug 26;9:922595. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.922595. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36090319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of systematic inflammatory and nutritional indexes in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer treated with first-line chemotherapy and atezolizumab.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021 Nov;70(11):3199-3206. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02926-3. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33796915 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing the length of stay after mediastinal tumor resection in the setting of an enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS)-TUBELESS protocol.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jun;8(12):740. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-287. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32647665 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) may be an effective indicator in predicting the left ventricular hypertrophy for patients diagnosed with hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 2023 May;37(5):379-385. doi: 10.1038/s41371-022-00755-0. Epub 2022 Sep 29. J Hum Hypertens. 2023. PMID: 36175554
-
Utility of prognostic nutritional index and systemic immune-inflammation index in oral cancer treatment.BMC Cancer. 2022 Apr 7;22(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09439-x. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35392843 Free PMC article.
-
The association of hemodynamic markers of right ventricular dysfunction with SII index and clinical outcomes in reduced ejection fraction heart failure.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 25;102(34):e34809. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034809. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37653803 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO: Fact sheet. World Health Organization. Accessed Feb 1 2017. Available from: http:// www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
-
- Huang QT, Zhou L, Zeng WJ. et al. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41:2411–2418. - PubMed
-
- Zhou WJ, Wu J, Li XD. et al. Effect of preoperative monocyte-lymphocyte ratio on prognosis of patients with resectable esophagogastric junction cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017;39:178–183. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

