An Experimentally Determined State Diagram for Human CD4+ T Lymphocyte CXCR4-Stimulated Adhesion Under Shear Flow
- PMID: 30271505
- PMCID: PMC6157745
- DOI: 10.1007/s12195-018-0519-x
An Experimentally Determined State Diagram for Human CD4+ T Lymphocyte CXCR4-Stimulated Adhesion Under Shear Flow
Abstract
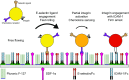
Introduction: The leukocyte adhesion cascade is important for the maintenance of homeostasis and the ability of immune cells to access sites of infection and inflammation. Despite much work identifying the molecular components of the cascade, and numerous simulations to predict the relationship between molecule density, identity, and adhesion, these relationships have not been measured experimentally.
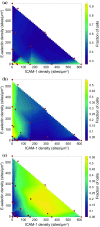
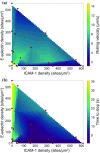
Methods: Using surfaces functionalized with recombinant ICAM-1 and/or E-selectin along with immobilized SDF-1α, we used a flow chamber to measure rates of tethering, rolling and arrest of primary naïve human CD4+ T lymphocytes on different surface densities of ligand.
Results: Cells required a minimum level of ligand density to progress beyond tethering. E-selectin and ICAM-1 were found to have a synergistic relationship in promoting cell arrest. Surfaces with both ligands had the highest levels of arrest, while surfaces containing only E-selectin hindered the cell's ability to progress beyond rolling. In contrast, surfaces of ICAM-1 allowed only tethering or arrest. Cells maintained constant rolling velocity and time to stop over large variations in surface density and composition. In addition, surface densities of only O(101) sites/μm2 allowed for rolling while surface densities of O(102) sites/μm2 promoted arrest, approximately equal to previously determined simulated values.
Conclusions: We have systematically and experimentally mapped out the state diagram of T-cell adhesion under flow, directly demonstrating the quantitative requirements for each dynamic state of adhesion, and showing how multiple adhesion molecules can act in synergy to secure arrest.
Keywords: CXCL12α; E-selectin; ICAM-1; SDF-1α; flow chamber; site density.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Nicholas R. Anderson, Dooyoung Lee, and Daniel A. Hammer declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
I-domain of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 mediates rolling of polystyrene particles on ICAM-1 under flow.Biophys J. 2005 Nov;89(5):3577-88. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.057729. Epub 2005 Aug 12. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16100282 Free PMC article.
-
Rolling of lymphocytes and neutrophils on peripheral node addressin and subsequent arrest on ICAM-1 in shear flow.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Apr;25(4):1025-31. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250425. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7537667
-
The chemokine SDF-1 stimulates integrin-mediated arrest of CD34(+) cells on vascular endothelium under shear flow.J Clin Invest. 1999 Nov;104(9):1199-211. doi: 10.1172/JCI7615. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10545519 Free PMC article.
-
Diacylglycerol kinase zeta negatively regulates CXCR4-stimulated T lymphocyte firm arrest to ICAM-1 under shear flow.Integr Biol (Camb). 2012 Jun;4(6):606-14. doi: 10.1039/c2ib00002d. Epub 2012 May 1. Integr Biol (Camb). 2012. PMID: 22546945
-
Neutrophil CD18-dependent arrest on intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) in shear flow can be activated through L-selectin.J Immunol. 1997 Jan 1;158(1):367-75. J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 8977212
Cited by
-
Adhesive dynamics simulations quantitatively predict effects of kindlin-3 deficiency on T-cell homing.Integr Biol (Camb). 2019 Jun 1;11(6):293-300. doi: 10.1093/intbio/zyz024. Integr Biol (Camb). 2019. PMID: 31329860 Free PMC article.
-
T lymphocytes migrate upstream after completing the leukocyte adhesion cascade.Cell Adh Migr. 2019 Dec;13(1):163-168. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2019.1587269. Epub 2019 Mar 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2019. PMID: 30879410 Free PMC article.
-
Human Neutrophils Will Crawl Upstream on ICAM-1 If Mac-1 Is Blocked.Biophys J. 2019 Oct 15;117(8):1393-1404. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.08.044. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 31585707 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Mapping of Adhesiveness on Live Cells Reveals How Guidance Phenotypes Can Emerge From Complex Spatiotemporal Integrin Regulation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 7;9:625366. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.625366. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33898401 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro Studies of Transendothelial Migration for Biological and Drug Discovery.Front Med Technol. 2020 Nov 16;2:600616. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2020.600616. eCollection 2020. Front Med Technol. 2020. PMID: 35047883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

