Microwave Ablation in Intermediate Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis: An Italian Multicenter Prospective Study
- PMID: 30271736
- PMCID: PMC6160301
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00013
Microwave Ablation in Intermediate Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis: An Italian Multicenter Prospective Study
Abstract
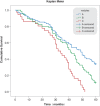
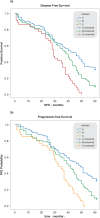
Background and Aims: To report long-term results in treatment of intermediate hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in cirrhotics using new high-powered microwaves (MWS) ablation alone. Methods: This multicenter study included 215 cirrhotics (age range: 67-84 years; 137 males; 149 Child A, 66 Child B) who underwent percutaneous ultrasound-guided high-powered MWS ablation instead of transarterial chemoembolization. Among the patient population, 109 had a single nodule (Ø 5.3-8 cm) [group A], 70 had 2 nodules (Ø 3-6 cm) [group B] and 36 had 3-5 nodules (Ø 1.5-6.8 cm) [group C]. MWS ablation efficacy was evaluated using enhanced-computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging. Primary end-point was 5-year cumulative overall survival (OS). Results: On enhanced-computed tomography and/or magnetic resonance imaging, complete ablation rates were 100% for 1.5-3.5 cm nodules. In nodules >3.5-5 cm, it was 89% for the first ablation and 100% for the second. For lesions >5-8 cm, ablation was up to 92%. Overall, 1-, 3- and 5-year survival rates were 89, 60, and 21%, respectively. The cumulative OS rate of group A was 89%, 66% and 34% at 1, 3 and 5 years. The cumulative OS rate of group B was 88%, 60% and 11% at 1, 3 and 5 years. The cumulative OS rate of group C was 86%, 55% and 0%. The 5-year survival rate was significantly different among the groups (p <0.001). One patient died from rupture of HCC. Upon multivariate analysis, preablation total bilirubin >1.5 mg/dL was an independent factor for predicting lower survival. Conclusions: Percutaneous MWS ablation of intermediate HCC is safe and effective in inducing large volume of necrosis in intermediate HCC nodules, providing long-term survival rates similar to transarterial chemoembolization. Preablation total bilirubin >1.5 mg/dL as expression of liver function reserve is the main factor predicting a worse outcome.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; HCC; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Intermediate stage; Microwaves ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver Resection versus Radiofrequency Ablation plus Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization in Cirrhotic Patients with Solitary Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017 Nov;28(11):1512-1519. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.06.016. Epub 2017 Jul 19. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28734848
-
Percutaneous thermal ablation of medium and large hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term outcome and prognostic factors.Cancer. 2009 May 1;115(9):1914-23. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24196. Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19241423
-
Comparison of albumin-bilirubin grade, platelet-albumin-bilirubin grade and Child-Turcotte-Pugh class for prediction of survival in patients with large hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):841-853. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2019.1646927. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 31452408
-
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous thermal ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma using microwave and radiofrequency ablation.Clin Radiol. 2004 Jan;59(1):53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2003.09.006. Clin Radiol. 2004. PMID: 14697375
-
The Combination Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation or Microwave Ablation against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019 Aug 26;2019:8619096. doi: 10.1155/2019/8619096. eCollection 2019. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31534899 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Thermal Ablation: Long-term Results of An Italian Retrospective Multicenter Study.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2019 Dec 28;7(4):287-292. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2019.00036. Epub 2019 Nov 27. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31915596 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant holmium-166 radioembolization after radiofrequency ablation in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a dose-finding study (HORA EST HCC trial).Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 Jun;51(7):2085-2097. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06630-z. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38329507 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Microwave Ablation Versus Nipple Sparing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer ≤5 cm: A Pilot Cohort Study.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 7;10:546883. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.546883. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33117685 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial comment: a review on radiofrequency, microwave and high-intensity focused ultrasound ablations for hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022 Jun;11(3):453-456. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-22-138. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35693404 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of patients with intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Nov 5;12:1758835920970840. doi: 10.1177/1758835920970840. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33224278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources