Conformational signatures in β-arrestin2 reveal natural biased agonism at a G-protein-coupled receptor
- PMID: 30272007
- PMCID: PMC6123711
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-018-0134-3
Conformational signatures in β-arrestin2 reveal natural biased agonism at a G-protein-coupled receptor
Abstract
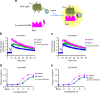
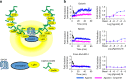
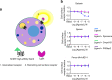
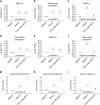
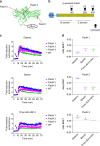
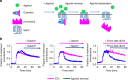
Discovery of biased ligands and receptor mutants allows characterization of G-protein- and β-arrestin-mediated signaling mechanisms of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). However, the structural mechanisms underlying biased agonism remain unclear for many GPCRs. We show that while Galanin induces the activation of the galanin receptor 2 (Galr2) that leads to a robust stimulation toward Gαq-protein and β-arrestin1/2, an alternative ligand Spexin and its analog have biased agonism toward G-protein signaling relative to Galanin. We used intramolecular fluorescein arsenical hairpin bioluminescence resonance energy transfer-based biosensors of β-arrestin2 combined with NanoBit technology to measure β-arrestin2-Galr2 interactions in real-time living systems. We found that Spexin and Galanin induce specific active conformations of Galr2, which may lead to different internalization rates of the receptor as well as different signaling outputs. This work represents an additional pharmacological evidence of endogenous G-protein-biased agonism at a GPCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Pierce KL, Premont RT, Lefkowitz RJ. Seven-transmembrane receptors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;9:639–650. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

