Gender-related differences in neural responses to gaming cues before and after gaming: implications for gender-specific vulnerabilities to Internet gaming disorder
- PMID: 30272247
- PMCID: PMC6234325
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsy084
Gender-related differences in neural responses to gaming cues before and after gaming: implications for gender-specific vulnerabilities to Internet gaming disorder
Abstract
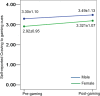
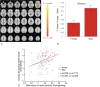
More males than females play video games and develop problems with gaming. However, little is known regarding how males and females who game on the Internet may differ with respect to neural responses to gaming cues. Behavioral and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data were recorded from 40 female and 68 male Internet gamers. This study included three components including participation in a pre-gaming cue-craving task, 30 min of online gaming and a post-gaming cue-elicited-craving task. Group differences were examined at pre-gaming, post-gaming and post- vs pre-gaming times. Correlations between brain responses and behavioral performance were calculated. : Gaming-related cues elicited higher cravings in male vs female subjects. Prior to gaming, males demonstrated greater activations in the striatum, orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), inferior frontal cortex and bilateral declive. Following gaming, male subjects demonstrated greater activations in the medial frontal gyrus and bilateral middle temporal gyri. In a post-pre comparison, male subjects demonstrated greater thalamic activation than did female subjects. Short-term gaming elicited in males vs females more craving-related activations to gaming cues. These results suggest neural mechanisms for why males may be more vulnerable than females in developing Internet gaming disorder.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gender-related differences in cue-elicited cravings in Internet gaming disorder: The effects of deprivation.J Behav Addict. 2018 Dec 1;7(4):953-964. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.118. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Behav Addict. 2018. PMID: 30556781 Free PMC article.
-
Sex difference in neural responses to gaming cues in Internet gaming disorder: Implications for why males are more vulnerable to cue-induced cravings than females.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Aug 24;760:136001. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136001. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 34090939
-
Gender-related functional connectivity and craving during gaming and immediate abstinence during a mandatory break: Implications for development and progression of internet gaming disorder.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Jan 10;88:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.04.009. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29684536
-
Internet Gaming Disorder: An Emergent Health Issue for Men.Am J Mens Health. 2018 Jul;12(4):1151-1159. doi: 10.1177/1557988318766950. Epub 2018 Apr 1. Am J Mens Health. 2018. PMID: 29606034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prefrontal dysfunction in individuals with Internet gaming disorder: a meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies.Addict Biol. 2015 Jul;20(4):799-808. doi: 10.1111/adb.12154. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24889021 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of resourcefulness on internet game addiction among college students: The mediating role of anxiety and the moderating role of gender.Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 13;11:986550. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.986550. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36860388 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Gaming Disorder with parenting based on low affection-communication and personality trait of neuroticism in adolescents.Front Psychol. 2023 Apr 27;14:1147601. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1147601. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37179866 Free PMC article.
-
The association between a stress-is-enhancing mindset and internet gaming disorder was mediated by behavioral disengagement among medical undergraduate students: a multi-center survey in China.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 May 12;25(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06910-4. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40355837 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Gaming Disorder, Self-Compensation Motivation, Game Flow, Time Spent Gaming, and Fear of Missing Out Among a Sample of Chinese University Students: A Network Analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Nov 1;12:761519. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.761519. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34790137 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in enhancing regulation of both craving and negative emotions in internet gaming disorder: A randomized trial.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020 Jul;36:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 May 21. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32446706 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edn, Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing.

