High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing
- PMID: 30275336
- PMCID: PMC6196543
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1811276115
High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing
Erratum in
-
Correction for Sago et al., High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 27;115(48):E11427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818262115. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30455314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
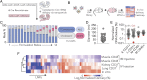
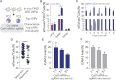
Dysfunctional endothelium causes more disease than any other cell type. Systemically administered RNA delivery to nonliver tissues remains challenging, in large part because there is no high-throughput method to identify nanoparticles that deliver functional mRNA to cells in vivo. Here we report a system capable of simultaneously quantifying how >100 lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) deliver mRNA that is translated into functional protein. Using this system (named FIND), we measured how >250 LNPs delivered mRNA to multiple cell types in vivo and identified 7C2 and 7C3, two LNPs that efficiently deliver siRNA, single-guide RNA (sgRNA), and mRNA to endothelial cells. The 7C3 delivered Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA to splenic endothelial cells as efficiently as hepatocytes, distinguishing it from LNPs that deliver Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA to hepatocytes more than other cell types. These data demonstrate that FIND can identify nanoparticles with novel tropisms in vivo.
Keywords: CRISPR; RNAi; barcoded nanoparticle; mRNA; nanoparticle.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: C.D.S., M.P.L., and J.E.D. have filed intellectual property related to this publication.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

