Impact of Sarcopenia as a Prognostic Biomarker of Bladder Cancer
- PMID: 30275370
- PMCID: PMC6213561
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19102999
Impact of Sarcopenia as a Prognostic Biomarker of Bladder Cancer
Abstract
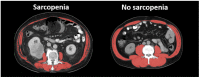
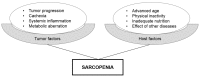
Sarcopenia, the degenerative and systemic loss of skeletal muscle mass, indicates patient frailty and impaired physical function. Sarcopenia can be caused by multiple factors, including advanced age, lack of exercise, poor nutritional status, inflammatory diseases, endocrine diseases, and malignancies. In patients with cancer cachexia, anorexia, poor nutrition and systemic inflammation make the metabolic state more catabolic, resulting in sarcopenia. Thus, sarcopenia is considered as one of manifestations of cancer cachexia. Recently, growing evidence has indicated the importance of sarcopenia in the management of patients with various cancers. Sarcopenia is associated with not only higher rates of treatment-related complications but also worse prognosis in cancer-bearing patients. In this article, we summarized metabolic backgrounds of cancer cachexia and sarcopenia and definitions of sarcopenia based on computed tomography (CT) images. We conducted a systematic literature review regarding the significance of sarcopenia as a prognostic biomarker of bladder cancer. We also reviewed recent studies focusing on the prognostic role of changes in skeletal muscle mass during the course of treatment in bladder cancer patients. Lastly, we discussed the impact of nutritional support, medication, and exercise on sarcopenia in cancer-bearing patients.
Keywords: biomarker; bladder cancer; prognosis; sarcopenia; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic and Molecular Basis of Sarcopenia: Implications in the Management of Urothelial Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 11;20(3):760. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030760. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30754663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of sarcopenia in the management of urological cancer patients.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017 May;17(5):455-466. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2017.1301209. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 28271727 Review.
-
Clinical impact of postoperative loss in psoas major muscle and nutrition index after radical cystectomy for patients with urothelial carcinoma of the bladder.BMC Cancer. 2017 Mar 31;17(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3231-7. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28359307 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle contractile and metabolic dysfunction is a common feature of sarcopenia of aging and chronic diseases: from sarcopenic obesity to cachexia.Clin Nutr. 2014 Oct;33(5):737-48. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24785098
-
Sarcopenia as a prognostic biomarker of advanced urothelial carcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 22;10(1):e0115895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115895. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25612215 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Systemic inflammation with sarcopenia predicts survival in patients with gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Mar;149(3):1249-1259. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-03925-2. Epub 2022 Apr 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35435489 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia as an independent predictor of the surgical outcomes of patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis.Surg Today. 2020 Oct;50(10):1138-1150. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01893-8. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Surg Today. 2020. PMID: 31617016 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcopenia is associated with leukopenia in urothelial carcinoma patients who receive tislelizumab combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin therapy.Int J Clin Oncol. 2024 May;29(5):592-601. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02448-1. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Int J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38514497 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Metabolic Markers of Bladder Cancer: A Reflection of the Tumor or the Response of the Body?Metabolites. 2021 Oct 31;11(11):756. doi: 10.3390/metabo11110756. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34822414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors Influencing Immunotherapy Outcomes in Cancer: Sarcopenia and Systemic Inflammation.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241302248. doi: 10.1177/10732748241302248. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39547932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellmunt J., von der Maase H., Mead G.M., Skoneczna I., De Santis M., Daugaard G., Boehle A., Chevreau C., Paz-Ares L., Laufman L.R., et al. Randomized phase III study comparing paclitaxel/cisplatin/gemcitabine and gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial cancer without prior systemic therapy: EORTC Intergroup Study 30987. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:1107–1113. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.6979. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical