Eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 30275848
- PMCID: PMC6157152
- DOI: 10.1186/s13223-018-0287-0
Eosinophilic esophagitis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Eosinophilic esophagitis.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019 Apr 10;15:22. doi: 10.1186/s13223-019-0336-3. eCollection 2019. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31007687 Free PMC article.
Abstract
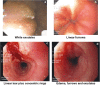
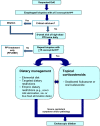
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an atopic condition of the esophagus that has become increasingly recognized over the last 15 years. Diagnosis of the disorder is dependent on the patient's clinical manifestations, and must be confirmed by histologic findings on esophageal mucosal biopsies. Patients with EoE should be referred to an allergist for optimal management, which may include dietary modifications and pharmacologic agents such as corticosteroids, and for the diagnosis and management of comorbid atopic conditions. Mechanical dilation of the esophagus may also be necessary. The epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of EoE are discussed in this review.
Figures
References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Katzka DA, American College of Gastroenterology ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(5):679–692. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.71. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

