EVALUATION OF VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL SACCADES USING THE DEVELOPMENTAL EYE MOVEMENT TEST COMPARED TO THE KING-DEVICK TEST
- PMID: 30276013
- PMCID: PMC6159500
EVALUATION OF VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL SACCADES USING THE DEVELOPMENTAL EYE MOVEMENT TEST COMPARED TO THE KING-DEVICK TEST
Abstract
Background: Oculomotor function is impaired when an individual has a concussion and as such, it is important to identify tests that are able to assess oculomotor impairment. The King-Devick (K-D) test assesses horizontal saccadic eye movement and attention. The Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) test is designed to identify oculomotor dysfunction in children. It measures both horizontal and vertical saccades. The K-D test shows promise as a concussion-screening tool and part of a multifactorial assessment. The DEM has not been tested as a concussion assessment tool, but the neuroanatomical control of horizontal and vertical saccades originates from different areas of the brain, so one might expect to see differences in performance on the K-D and DEM tests when administered to concussed patients. First, it is important to determine if performance on the DEM and K-D tests, particularly with respect to the measurement of vertical and horizontal saccades, is similar in a healthy population.Hypothesis/Purpose: The primary purpose was to evaluate the relationship between horizontal and vertical saccade tests over repeated trials in normal, healthy subjects. A secondary purpose of this study was to determine the number of trials needed to reach a performance plateau for both the DEM and K-D tests.Study Design: This study used a prospective cohort research design.
Methods: Forty-two healthy non-concussed participants (22 males, 20 females; mean age, 24.2 ± 2.92 years) completed six repeated trials of both the DEM, and then six trials of the K-D test in a single testing session. Trials within each test were performed in random order and participants were offered short rest breaks as needed between test administrations.
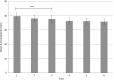
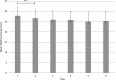
Results: Results indicated strong correlations, r=.67, or greater, between measurements of horizontal and vertical saccades. Performance plateaued on the K-D at trial three and on the DEM at trial two for both horizontal and vertical saccades.
Conclusion: It appears that the DEM and K-D tests measure similar constructs in healthy individuals and that no additional information is provided by assessment of vertical saccades. Additional studies are required to investigate the usefulness of the DEM in concussed individuals.
Level of evidence: 3: Laboratory study with repeated measures.
Keywords: Concussion baseline testing; ocular motor dysfunction; saccades.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of two visual-verbal tests of ocular motility using an eye-tracker.J Optom. 2024 Oct-Dec;17(4):100517. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2024.100517. Epub 2024 Jun 21. J Optom. 2024. PMID: 38908038 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) and King-Devick (K-D) Performance in Multiple Sclerosis.Brain Sci. 2022 Jul 20;12(7):954. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12070954. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35884760 Free PMC article.
-
In situ use of the King-Devick eye tracking test and changes seen with sport-related concussion: saccadic and blinks counts.Phys Sportsmed. 2019 Feb;47(1):78-84. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2018.1525261. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Phys Sportsmed. 2019. PMID: 30244636
-
Assessment of vision in concussion.Curr Opin Neurol. 2019 Feb;32(1):68-74. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000654. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30516648 Review.
-
The King-Devick test of rapid number naming for concussion detection: meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature.Concussion. 2015 Sep 10;1(2):CNC8. doi: 10.2217/cnc.15.8. eCollection 2016 Mar. Concussion. 2015. PMID: 30202552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of two visual-verbal tests of ocular motility using an eye-tracker.J Optom. 2024 Oct-Dec;17(4):100517. doi: 10.1016/j.optom.2024.100517. Epub 2024 Jun 21. J Optom. 2024. PMID: 38908038 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Eye Movement (DEM) Test in Adults: Age-Related Changes and Italian Normative Data.Vision (Basel). 2025 Feb 2;9(1):10. doi: 10.3390/vision9010010. Vision (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39982327 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and Integration of Cervical Manual Therapy and Vestibulo-oculomotor Therapy for Concussion Symptoms: Retrospective Analysis.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021 Feb 1;16(1):12-20. doi: 10.26603/001c.18825. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2021. PMID: 33604130 Free PMC article.
-
The University of Kansas Health System Outpatient Clinical Concussion Comprehensive Protocol: An Interdisciplinary Approach.Health Serv Insights. 2022 Aug 23;15:11786329221114759. doi: 10.1177/11786329221114759. eCollection 2022. Health Serv Insights. 2022. PMID: 36034733 Free PMC article.
-
Visual fixations rather than saccades dominate the developmental eye movement test.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):1162. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80870-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langlois JA Rutland-Brown W Wald MM. The epidemiology and impact of traumatic brain injury: a brief overview. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2006;21(5):375-378. - PubMed
-
- Galetta KM Brandes LE Maki K, et al. The King-Devick test and sports-related concussion: study of a rapid visual screening tool in a collegiate cohort. J Neurol Sci. 2011;309(1-2):34-39. - PubMed
-
- Ventura RE Balcer LJ Galetta SL. The neuro-ophthalmology of head trauma. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(10):1006-1016. - PubMed
-
- Vartiainen MV Holm A Peltonen K Luoto TM Iverson GL Hokkanen L. King-Devick test normative reference values for professional male ice hockey players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
