The Cytotoxic and Antimigratory Activity of Brazilin-Doxorubicin on MCF-7/HER2 Cells
- PMID: 30276148
- PMCID: PMC6156471
- DOI: 10.15171/apb.2018.059
The Cytotoxic and Antimigratory Activity of Brazilin-Doxorubicin on MCF-7/HER2 Cells
Abstract
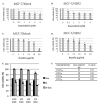
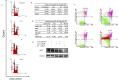
Purpose: Breast cancer cells with overexpression of HER2 are known to be more aggressive, invasive, and resistant to chemotherapeutic agent. Brazilin, the major compound in the Caesalpinia sappan L. (CS) heartwood, has been studied for it's anticancer activity. The purpose of this study was to investigate the cytotoxic and antimigratory activity of brazilin (Bi) in combination with doxorubicin (Dox) on MCF-7/HER2 cells. Methods: Cytotoxic activities of Bi individually and in combination with Dox were examined by MTT assay. Synergistic effects were analyzed by combination index (CI). Apoptosis and cell cycle profiles were observed by using flow cytometry. Migrating and invading cells were observed by using a Boyden chamber assay. Levels of MMP2 and MMP9 activity were observed by using a gelatin zymography assay. Levels of HER2, Bcl-2, Rac1, and p120 protein expression were observed by using an immunoblotting assay. Results: The results of the MTT assay showed that Bi inhibited MCF-7/HER2 cell growth in a dose-dependent manner with an IC50 of 54 ± 3.7 µM. Furthermore, the combination of Bi and Dox showed a synergistic effect (CI <1). Flow cytometric analysis of Bi and its combination with Dox showed cellular accumulation in the G2/M phase and induction of apoptosis through suppression of Bcl-2 protein expression. In the Boyden chamber assay, gelatin zymography, and subsequent immunoblotting assay, the combination Bi and Dox inhibited migration, possibly through downregulation of MMP9, MMP2, HER2, Rac1, and p120 protein expression. Conclusion: We conclude that Bi enhanced cytotoxic activity of Dox and inhibited migration of MCF-7/HER2 cells. Therefore, we believe that it has strong potential to be developed for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer with HER2 overexpression.
Keywords: Brazilin; Cytotoxic effect; Doxorubicin; MCF-7/HER2 cells; Migration.
Similar articles
-
Synergistic Cytotoxic and Antimigratory Effect of Brazilein and Doxorubicin on HER2-Overexpressing Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Aug 1;23(8):2623-2632. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.8.2623. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36037115 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic and Antimetastatic Activity of Hesperetin and Doxorubicin Combination Toward Her2 Expressing Breast Cancer Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 May 1;21(5):1259-1267. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.5.1259. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32458631 Free PMC article.
-
Two Active Compounds from Caesalpinia sappan L. in Combination with Cisplatin Synergistically Induce Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest on WiDr Cells.Adv Pharm Bull. 2017 Sep;7(3):375-380. doi: 10.15171/apb.2017.045. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 29071219 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilin: Biological activities and therapeutic potential in chronic degenerative diseases and cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2022 Jan;175:106023. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106023. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Pharmacol Res. 2022. PMID: 34883212 Review.
-
Article review: Brazilin as potential anticancer agent.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 7;15:1355533. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1355533. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38515856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Cytotoxic and Antimigratory Effect of Brazilein and Doxorubicin on HER2-Overexpressing Cells.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Aug 1;23(8):2623-2632. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.8.2623. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36037115 Free PMC article.
-
RepCOOL: computational drug repositioning via integrating heterogeneous biological networks.J Transl Med. 2020 Oct 2;18(1):375. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02541-3. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33008415 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Anti-Tumor potential and safety of application of Glutathione stabilized Gold Nanoparticles conjugated with Chemotherapeutics.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Mar 12;17(6):824-833. doi: 10.7150/ijms.40827. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32218704 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro synergistic effect of hesperidin and doxorubicin downregulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in highly metastatic breast cancer cells.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2023 Mar 27;35(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s43046-023-00166-3. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2023. PMID: 36967442
-
Protosappanin B Exerts Anti-tumor Effects on Colon Cancer Cells via Inhibiting GOLPH3 Expression.Integr Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1534735420972477. doi: 10.1177/1534735420972477. Integr Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 33289438 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous