NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 30277570
- PMCID: PMC6194337
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13167
NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
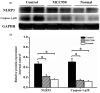
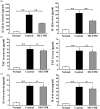
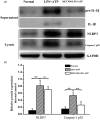
Nucleotide-binding, oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor family, pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) gene polymorphism was reported to be associated with susceptibility, disease activity or anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in the development of RA have not yet been elucidated fully. The present study aimed to study the role of NLRP3 inflammasome in RA. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in synovial tissues from RA and osteoarthritis (OA) patients were assessed by Western blot. Active caspase-1 in synovia was stained by a FAM-FLICA caspase-1 probe. Mice with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) were treated with MCC950, a selective NLRP3 inhibitor, or vehicle for 2 weeks. The clinical score of arthritis, synovial inflammation and cartilage erosion were assessed. Proinflammatory cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The results showed that NLRP3 inflammasome was highly activated in both synovia from RA patients and CIA mice. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome occurred mainly in the infiltrating monocyte/macrophages in synovia, but not in fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Treatment with MCC950 resulted in significantly less severe joints inflammation and bone destruction. NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the synovia was inhibited significantly by MCC950 with reduced production of interleukin (IL)-1β. The inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by MCC950 was confirmed further in a human monocytic cell line, THP-1. In conclusion, NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in the pathogenesis of RA. Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome with a small molecule inhibitor might be a novel therapeutic strategy for RA.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; NLRP3 inhibitor; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2018 British Society for Immunology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resveratrol reduces the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in rheumatoid arthritis through SIRT1 and ITGB α5β1, especially in patients with high expression of ACPA.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156897. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156897. Epub 2025 May 29. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40480022
-
TNF-α/calreticulin dual signaling induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation associated with HuR nucleocytoplasmic shuttling in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflamm Res. 2019 Jul;68(7):597-611. doi: 10.1007/s00011-019-01244-w. Epub 2019 May 22. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 31119302
-
Tofacitinib restores the balance of γδTreg/γδT17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 1;11(3):1446-1457. doi: 10.7150/thno.47860. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33391544 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and synthetic potential drug leads for rheumatoid arthritis probing innovative target: mitochondrial dysfunction and NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8295-8312. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03897-3. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40019529 Review.
-
The role of mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation.Mol Immunol. 2018 Nov;103:115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30248487 Review.
Cited by
-
Triterpenes Drug Delivery Systems, a Modern Approach for Arthritis Targeted Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 28;17(1):54. doi: 10.3390/ph17010054. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 and its Multifaceted Impact on Bone Health: Mechanisms and Clinical Evidence.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024 Feb;22(1):135-145. doi: 10.1007/s11914-023-00843-1. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2024. PMID: 38236510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linear ubiquitination of LKB1 activates AMPK pathway to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome response and reduce chondrocyte pyroptosis in osteoarthritis.J Orthop Translat. 2022 Dec 1;39:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2022.11.002. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2022. PMID: 36514784 Free PMC article.
-
Causal Biological Network Model for Inflammasome Signaling Applied for Interpreting Transcriptomic Changes in Various Inflammatory States.Int J Inflam. 2022 Jan 27;2022:4071472. doi: 10.1155/2022/4071472. eCollection 2022. Int J Inflam. 2022. PMID: 35126992 Free PMC article.
-
New Druggable Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis Based on Insights From Synovial Biology.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 21;13:834247. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.834247. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35265082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–19. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016;388:2023–38. - PubMed
-
- Siebert S, Tsoukas A, Robertson J, McInnes I. Cytokines as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. Pharmacol Rev. 2015;67:280–309. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42. - PubMed
-
- Dayer JM. The pivotal role of interleukin‐1 in the clinical manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxf). 2003;42:3ii‐10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

