Red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio as a disease activity-associated factor in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 30278511
- PMCID: PMC6181617
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012342
Red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio as a disease activity-associated factor in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Although different clinical and experimental parameters have been used to estimate disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients, the relationship between red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio (RPR) and disease activity in SLE has not been previously illuminated. Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the association between RPR levels and disease activity in SLE.
Methods: This study enrolled 105 SLE patients and 105 healthy subjects. We divided the patients into 2 groups using the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) 2000. Group 1 included patients with SLEDAI score ≤9 (mild disease activity group) and group 2 with SLEDAI >9 (severe disease activity group). Correlations between RPR and disease activity were then analyzed. A subgroup follow-up analysis of 93 patients was conducted to explore the effect of SLE-related glucocorticoid therapy.
Results: The PLR and RPR values of SLE patients were significantly higher compared with the controls (both P < .001), whereas mean platelet volume was decreased (P < .05). The RPR level was found to be positively correlated with SLEDAI (r = 0.368, P < .001) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (r = 0.313, P = .027). According to the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve, the optimal cut-off value for predicting SLE using RPR was 0.073, and the area under ROC curve was 0.817. RPR level was correlated with clinical disease activity in SLE, and its value was normalized after treatment.
Conclusion: RPR may be a useful measurement for the assessment of disease activity in SLE patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

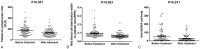


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of red blood cell distribution width-platelet ratio as a predictor of adverse pregnancy outcomes and disease severity in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Rheumatol. 2022 Oct;41(10):2987-2993. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06169-0. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Clin Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35788840
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients.Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(3):372-6. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1091136. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26403379
-
Red blood cell distribution width is a potential index to assess the disease activity of systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Oct 21;425:202-5. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.007. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23954839
-
Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a biomarker of systemic inflammation in systemic lupus erythematosus: A meta-analysis and systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 May 16;19(5):e0303665. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303665. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38753735 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with activity: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105949. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105949. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31634817
Cited by
-
The Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as an Inflammatory Marker in Rheumatic Diseases.Ann Lab Med. 2019 Jul;39(4):345-357. doi: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.4.345. Ann Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 30809980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of peripheral blood cells on ischemic stroke: Greater immune response or systemic inflammation?Heliyon. 2024 May 29;10(11):e32171. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32171. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38868036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mean Platelet Volume-to-Platelet Count Ratio, Mean Platelet Volume-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-Platelet Count Ratio as Markers of Inflammation in Patients with Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Apr 1;35(2):175-180. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2019-0348. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32369297 Free PMC article.
-
An Evaluation of the Different Serum Markers Associated with Mortality in Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever.Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2020 Oct 14;11(4):e0032. doi: 10.5041/RMMJ.10393. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 2020. PMID: 32077849 Free PMC article.
-
A Prognostic Model Incorporating Relevant Peripheral Blood Inflammation Indicator to Predict Postherpetic Neuralgia in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster.J Pain Res. 2024 Jul 1;17:2299-2309. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S466939. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38974827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danchenko N, Satia JA, Anthony MS. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 2006;15:308–18. - PubMed
-
- Quartier P, A-M P. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2004;23:111.
-
- Goodnow CC. Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell 2007;130:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Zivković V, Stanković A, Cvetković T, et al. Anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-C1q antibodies as disease activity markers in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Srpski Arhiv Za Celokupno Lekarstvo 2014;142:431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

