Physical Activity and Gastric Cancer Risk in Patients with and without Helicobacter pylori Infection in A Korean Population: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study
- PMID: 30279385
- PMCID: PMC6210303
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10100369
Physical Activity and Gastric Cancer Risk in Patients with and without Helicobacter pylori Infection in A Korean Population: A Hospital-Based Case-Control Study
Abstract
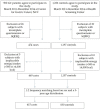
Although physical activity (PA) is beneficial for prolonging lifespan, evidence for the protective role of PA against the development of gastric cancer (GC) is not yet well established. This study assessed the association between PA and GC risk in patients with and without Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in a Korean population. In total, 415 GC patients and 830 controls were enrolled at the National Cancer Center, Korea. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire-Short Form was used to collect PA data. The odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated using unconditional logistic regression models. In the H. pylori-positive group, subjects who engaged in regular exercise showed a significantly reduced risk of GC in the entire population (OR = 0.52, 95% CI = 0.38⁻0.70) and in females (OR = 0.60, 95% CI = 0.21⁻0.64). Subjects who engaged in a high level of total PA showed a significantly reduced risk of GC relative to subjects in the lowest tertile in the fully adjusted model (OR = 0.46, 95% CI = 0.32⁻0.65, p-trend < 0.001). There was an inverse association between PA and GC risk in the entire population, and in the H. pylori-positive subgroup. Our data indicate the need for the promotion of all domains of PA, especially for Korean populations.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori infection; gastric cancer; physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of alcohol consumption, ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism, and Helicobacter pylori infection on the gastric cancer risk in a Korean population.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6630-6641. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14250. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036260 Free PMC article.
-
Association analysis between SNPs in LATS1 and LATS2 and non-cardia gastric cancer.BMC Gastroenterol. 2020 May 18;20(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s12876-020-01250-x. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32423384 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk of gastric cancer in the Korean population: prospective case-controlled study.J Gastroenterol. 2001 Dec;36(12):816-22. doi: 10.1007/s005350170003. J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11777209
-
Association between Helicobacter pylori antibodies determined by multiplex serology and gastric cancer risk: A meta-analysis.Helicobacter. 2022 Jun;27(3):e12881. doi: 10.1111/hel.12881. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Helicobacter. 2022. PMID: 35212073 Review.
-
Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on the incidence of gastric cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Gastric Cancer. 2019 May;22(3):435-445. doi: 10.1007/s10120-018-0876-0. Epub 2018 Sep 11. Gastric Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30206731
Cited by
-
Association between physical activity and digestive-system cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.J Sport Health Sci. 2021 Jan;10(1):4-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jshs.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Sep 30. J Sport Health Sci. 2021. PMID: 33010525 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Dietary Pattern Networks Associated with Gastric Cancer Using Gaussian Graphical Models: A Case-Control Study.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 23;12(4):1044. doi: 10.3390/cancers12041044. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32340406 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity modified the association of blood cadmium and lead with Helicobacter pylori infection: A cross-sectional analysis with NHANES data.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 11;103(41):e39899. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039899. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465795 Free PMC article.
-
Association between metabolic syndrome and gastric cancer risk: results from the Health Examinees Study.Gastric Cancer. 2023 Jul;26(4):481-492. doi: 10.1007/s10120-023-01382-5. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Gastric Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37010633
-
The association between physical activity and risk of gastric cancer; an umbrella review.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug 12;24(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03360-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39135152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold M., Karim-Kos H.E., Coebergh J.W., Byrnes G., Antilla A., Ferlay J., Renehan A.G., Forman D., Soerjomataram I. Recent trends in incidence of five common cancers in 26 European countries since 1988: Analysis of the European cancer observatory. Eur. J. Cancer. 2015;51:1164–1187. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2013.09.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Forman D., Bray F., Brewster D., Gombe Mbalawa C., Kohler B., Piñeros M., Steliarova-Foucher E., Swaminathan R., Ferlay J. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, Vol. X (Electronic Version) IARC; Lyon, France: 2013. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous