Discovery of Novel Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors as Potent Vasodilators
- PMID: 30279487
- PMCID: PMC6168526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32449-4
Discovery of Novel Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors as Potent Vasodilators
Abstract
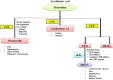
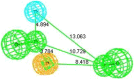
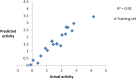
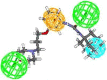
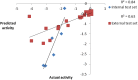
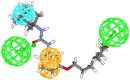
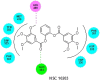
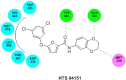
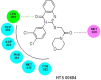
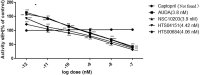
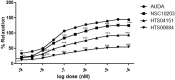
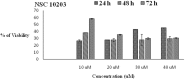
In view of the role of sEH (soluble epoxide hydrolase) in hypertension, we have developed a rigorously validated pharmacophore model containing one HBA (Hydrogen Bond Acceptor), two HY (Hydrophobic) and one RA (Ring Aromatic) features. The model was used as a query to search the NCI (National Cancer Institute) and Maybridge database leading to retrieval of many compounds which were sorted on the basis of predicted activity, fit value and Lipinski's violation. The selected compounds were docked into the active site of enzyme soluble epoxide hydrolase. Potential interactions were observed between the features of the identified hits and the amino acids present in the docking site. The three selected compounds were subjected to in vitro evaluation using enzyme- based assay and the isolated rat aortic model followed by cytotoxicity studies. The results demonstrate that the identified compounds are potent, safe and novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
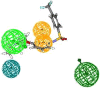
Similar articles
-
Pharmacophore based virtual screening, molecular docking and biological evaluation to identify novel PDE5 inhibitors with vasodilatory activity.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jul 15;24(14):3137-41. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.05.004. Epub 2014 May 14. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014. PMID: 24856068
-
Investigation of the binding mode of 1, 3, 4-oxadiazole derivatives as amide-based inhibitors for soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) by molecular docking and MM-GBSA.Eur Biophys J. 2017 Jul;46(5):445-459. doi: 10.1007/s00249-016-1188-0. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Eur Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 27928588
-
Discovery of Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitors by Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening.J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Apr 25;56(4):747-62. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.5b00592. Epub 2016 Apr 4. J Chem Inf Model. 2016. PMID: 26882208
-
Soluble epoxide hydrolase, a target with multiple opportunities for cardiovascular drug discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2009;9(5):452-63. doi: 10.2174/156802609788340805. Curr Top Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19519461 Review.
-
The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical target for hypertension.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;50(3):225-37. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181506445. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17878749 Review.
Cited by
-
Increased Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Activity Positively Correlates with Mortality in Heart Failure Patients with Preserved Ejection Fraction: Evidence from Metabolomics.Phenomics. 2022 Oct 27;3(1):34-49. doi: 10.1007/s43657-022-00069-8. eCollection 2023 Feb. Phenomics. 2022. PMID: 36939801 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin ameliorates oxidative stress levels in HepG2 cells and hyperlipidemic rats.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Jan 28;3:100088. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100088. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 35146420 Free PMC article.
-
Subnormothermic Machine Perfusion of Steatotic Livers Results in Increased Energy Charge at the Cost of Anti-Oxidant Capacity Compared to Normothermic Perfusion.Metabolites. 2019 Oct 24;9(11):246. doi: 10.3390/metabo9110246. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31652927 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory of disenecionyl cis-khellactone in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and the its inhibitory activity on soluble epoxide hydrolase.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 14;9(10):e21032. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21032. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37876448 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-Sensitive Hypertension in GR+/- Rats Is Accompanied with Dysregulation in Adrenal Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 8;22(24):13218. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413218. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Behm DJ, Ogbonna A, Wu C, Burns-Kurtis CL, Douglas SA. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids function as selective, endogenous antagonists of native thromboxane receptors: identification of a novel mechanism of vasodilation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009;328:231–239. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.145102. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Falck JR, Harris RC. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation. Molecular and functional properties of the arachidonatemonooxygenase. J. Lipid. Res. 2000;41:163–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

