Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
- PMID: 30279532
- PMCID: PMC6168530
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06533-2
Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 7;12(1):357. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20668-1. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33414450 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Oxidative stress plays an important role in the pathogenesis of many disease states. In the heart, reactive oxygen species are linked with cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury, hypertrophy, and heart failure. While this correlation between ROS and cardiac pathology has been observed in multiple models of heart failure, the independent role of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in vitro and in vivo is unclear, owing to a lack of tools for precise manipulation of intracellular redox state. Here we apply a chemogenetic system based on a yeast D-amino acid oxidase to show that chronic generation of H2O2 in the heart induces a dilated cardiomyopathy with significant systolic dysfunction. We anticipate that chemogenetic approaches will enable future studies of in vivo H2O2 signaling not only in the heart, but also in the many other organ systems where the relationship between redox events and physiology remains unclear.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
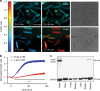
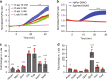



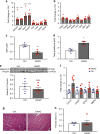
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5T32HL007604/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- PO1-HL48743/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- R01 HL046457/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 9-17-CMF-012/American Diabetes Association (ADA)/International
- P01 HL048743/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008313/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RO1-HL46457/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- T32-GM007753/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)/International
- T32 HL007604/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

