Genetic disruption of calpain-1 and calpain-2 attenuates tumorigenesis in mouse models of HER2+ breast cancer and sensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin and lapatinib
- PMID: 30279968
- PMCID: PMC6161787
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.26078
Genetic disruption of calpain-1 and calpain-2 attenuates tumorigenesis in mouse models of HER2+ breast cancer and sensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin and lapatinib
Abstract
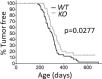
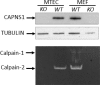
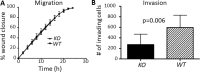
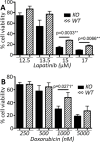
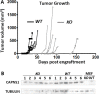
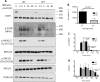
Calpains are a family of calcium activated cysteine proteases which participate in a wide range of cellular functions including migration, invasion, autophagy, programmed cell death, and gene expression. Calpain-1 and calpain-2 isoforms are ubiquitously expressed heterodimers composed of isoform specific catalytic subunits coupled with an obligate common regulatory subunit encoded by capns1. Here, we report that conditional deletion of capns1 disrupted calpain-1 and calpain-2 expression and activity, and this was associated with delayed tumorigenesis and altered signaling in a transgenic mouse model of spontaneous HER2+ breast cancer and effectively blocked tumorigenesis in an orthotopic engraftment model. Furthermore, capns1 knockout in a tumor derived cell line correlated with enhanced sensitivity to the chemotherapeutic doxorubicin and the HER2/EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib. Collectively, these results indicate pro-tumorigenic roles for calpains-1/2 in HER2+ breast cancer and provide evidence that calpain-1/2 inhibitors could have anti-tumor effects if used either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutics and targeted agents.
Keywords: HER2; breast cancer; calpain; capns1.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Calpain as a novel regulator of autophagosome formation.Autophagy. 2007 May-Jun;3(3):235-7. doi: 10.4161/auto.3661. Epub 2007 May 6. Autophagy. 2007. PMID: 17224628
-
The calpain system as a modulator of stress/damage response.Cell Cycle. 2007 Jan 15;6(2):136-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.6.2.3759. Epub 2007 Jan 27. Cell Cycle. 2007. PMID: 17264674 Review.
-
NRF-1, and AP-1 regulate the promoter of the human calpain small subunit 1 (CAPNS1) gene.Gene. 2008 Feb 29;410(1):197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.12.009. Epub 2007 Dec 23. Gene. 2008. PMID: 18234454
-
Conditional disruption of ubiquitous calpains in the mouse.Genesis. 2006 Jun;44(6):297-303. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20216. Genesis. 2006. PMID: 16783822
-
Calpain as a therapeutic target in cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022 Mar;26(3):217-231. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2022.2047178. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2022. PMID: 35225722 Review.
Cited by
-
Calpain-mediated Mechanoptosis in Breast Adenocarcinoma.Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023 May 3;3(3):297-301. doi: 10.21873/cdp.10215. eCollection 2023 May-Jun. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2023. PMID: 37168957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpains, the proteases of two faces controlling the epithelial homeostasis in mammary gland.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Sep 19;11:1249317. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1249317. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37795261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification and structure-function analysis of calpain-1 and calpain-2 protease subunit interactions.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jun;301(6):110243. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110243. Epub 2025 May 16. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40383147 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria in tumor immune surveillance and tumor therapies targeting mitochondria.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Dec;47(6):2031-2047. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-01000-1. Epub 2024 Oct 7. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 39373857 Review.
-
Targeted inhibition of endothelial calpain delays wound healing by reducing inflammation and angiogenesis.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jul 14;11(7):533. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02737-x. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32665543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell RL, Davies PL. Structure-function relationships in calpains. Biochem J. 2012;447:335–51. - PubMed
-
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:731–801. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K, Sorimachi H, Yoshizawa T, Kinbara K, Ishiura S. Calpain: novel family members, activation, and physiologic function. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1995;376:523–9. - PubMed
-
- Ono Y, Saido TC, Sorimachi H. Calpain research for drug discovery: challenges and potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:854–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

