A study on medical Internet of Things and Big Data in personalized healthcare system
- PMID: 30279984
- PMCID: PMC6146872
- DOI: 10.1007/s13755-018-0049-x
A study on medical Internet of Things and Big Data in personalized healthcare system
Abstract
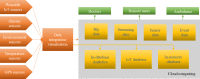
Personalized healthcare systems deliver e-health services to fulfill the medical and assistive needs of the aging population. Internet of Things (IoT) is a significant advancement in the Big Data era, which supports many real-time engineering applications through enhanced services. Analytics over data streams from IoT has become a source of user data for the healthcare systems to discover new information, predict early detection, and makes decision over the critical situation for the improvement of the quality of life. In this paper, we have made a detailed study on the recent emerging technologies in the personalized healthcare systems with the focus towards cloud computing, fog computing, Big Data analytics, IoT and mobile based applications. We have analyzed the challenges in designing a better healthcare system to make early detection and diagnosis of diseases and discussed the possible solutions while providing e-health services in secure manner. This paper poses a light on the rapidly growing needs of the better healthcare systems in real-time and provides possible future work guidelines.
Keywords: Big Data analytics; Cloud computing; Fog computing; Healthcare system; Internet of Things; Mobile computing; Security; Sensors.
Figures
References
-
- Ali Z, Hossain MS, Muhammad G, Sangaiah AK. An intelligent healthcare system for detection and classification to discriminate vocal fold disorders. Future Gen Comput Syst. 2018;85:19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.02.021. - DOI
-
- Yang G, et al. A health-IoT platform based on the integration of intelligent packaging, unobtrusive bio-sensor, and intelligent medicine box. IEEE Trans Ind Inform. 2014;10(4):2180–2191. doi: 10.1109/TII.2014.2307795. - DOI
-
- Yan Y, Li Q, Li H, Zhang X, Wang L. Open Access: A home-based health information acquisition system. Health Inform Sci Syst. 2013;1:12. doi: 10.1186/2047-2501-1-12. - DOI
-
- Khan M, Han K, Karthik S. Designing smart control systems based on Internet of Things and Big Data analytics. Wirel Pers Commun. 2018;99(4):1683–1697. doi: 10.1007/s11277-018-5336-y. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources