Idiopathic Charcot Arthropathy of the Knee Presenting as a Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
- PMID: 30280143
- PMCID: PMC6145554
- DOI: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-18-00032
Idiopathic Charcot Arthropathy of the Knee Presenting as a Bicondylar Tibial Plateau Fracture
Abstract
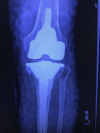
Charcot arthropathy is an infrequent condition that primarily involves the foot and ankle; rarely, it has been reported to affect the knee. Risk factors for Charcot arthropathy are well described with diabetes being the most common cause. Idiopathic Charcot arthropathy without a secondary etiology is extremely rare, with only a few cases described involving the foot and shoulder. Clinically, idiopathic Charcot arthropathy presents a notable challenge because delayed diagnosis can lead to surgical complications and advancement of joint destruction. We report idiopathic Charcot arthropathy of the knee presenting as a bicondylar tibial plateau fracture successfully managed with total knee arthroplasty after failed open reduction internal fixation. We diagnosed the patient when the clinical/surgical presentation was indicative of Charcot arthropathy and after excluding all other diagnoses. This previously unreported case describes the complexity of idiopathic Charcot arthropathy with subsequent fractures and highlights the importance of patient history, presentation, and surgical intervention.
Figures


References
-
- Bariteau J, Tenenbaum S, Rabinovich A, Brodsky J: Charcot arthropathy of the foot and ankle in patients with idiopathic neuropathy. Foot Ankle Int 2014;35:996-1001. - PubMed
-
- Blanford AT, Keane SP, McCarty DJ, Albers JW: Idiopathic Charcot joint of the elbow. Arthritis Rheum 1978;21:723-726. - PubMed
-
- Zeng M, Xie J, Hu Y: Total knee arthroplasty in patients with Charcot joints. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2016;24:2672-2677. - PubMed
-
- Kugelman D, Qatu A, Haglin J, Leucht P, Konda S, Egol K: Complications and unplanned outcomes following operative treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Injury 2017;48:2221-2229. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

