Rapid differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus subspecies based on MALDI-TOF MS profiles
- PMID: 30280650
- PMCID: PMC6505833
- DOI: 10.1177/1040638718805537
Rapid differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus subspecies based on MALDI-TOF MS profiles
Abstract
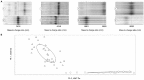
Staphylococcus aureus encompasses 2 subspecies ( aureus and anaerobius) with significant differences in their epidemiology and pathogenicity. We evaluated the suitability of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for the rapid identification of both subspecies using a panel of 52 S. aureus isolates (30 subsp. anaerobius and 22 subsp. aureus) recovered from different origins, countries, and years. The on-board library identification system correctly identified 42 of 52 (81%) S. aureus isolates at the species level with score values >2.0. Limited performance was observed for differentiation of S. aureus subspecies (particularly subsp. anaerobius). Visual inspection of MALDI-TOF MS profiles identified 5 subspecies-specific mass peaks ( m/ z 3430 and 6861 in S. aureus subsp. anaerobius, and m/ z 4046, 6890, and 8093 in S. aureus subsp. aureus) with 100% sensitivity and specificity values, which is potentially useful for differentiating these subspecies. The suitability of 3 models, Genetic Analysis (GA), Quick Classifier (QC), and Supervised Neural Network, for automatic identification of both subspecies was evaluated using the Recognition Capability (RC) and Cross Validation (CV) values provided by the on-board ClinProTools software. The GA and QC models reached RC and CV values of 100%. Both models were externally validated using a panel of 26 S. aureus isolates of both subspecies, with both models correctly classifying all isolates of both subspecies. MALDI-TOF MS coupled with ClinProTools software represents a rapid and simple approach for S. aureus subspecies discrimination.
Keywords: MALDI-TOF MS; Staphylococcus aureus subspecies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bergeron M, et al. Species identification of staphylococci by amplification and sequencing of the tuf gene compared to the gap gene and by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2011;30:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand X, et al. First report of a catalase-negative methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2002;43:45–46. - PubMed
-
- Chessa D, et al. An overview of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus with a focus on developing countries. J Infect Dev Ctries 2015;9:547–550. - PubMed
-
- Cho Y, et al. Rapid and accurate identification of species of the genus Pediococcus isolated from Korean fermented foods by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight MS with local database extension. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2017;67:744–752. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

