Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients
- PMID: 30281132
- PMCID: PMC6168816
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfy174
Cardiovascular disease in dialysis patients
Abstract
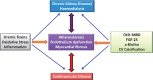
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a highly common complication and the first cause of death in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on haemodialysis (HD). In this population, mortality due to CVD is 20 times higher than in the general population and the majority of maintenance HD patients have CVD. This is likely due to ventricular hypertrophy as well as non-traditional risk factors, such as chronic volume overload, anaemia, inflammation, oxidative stress, chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder and other aspects of the 'uraemic milieu'. Better understanding the impact of these numerous factors on CVD would be an important step for prevention and treatment. In this review we focus non-traditional CVD risk factors in HD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Cozzolino M, Galassi A, Pivari F. et al. The cardiovascular burden in end-stage renal disease. Contrib Nephrol 2017; 191: 44–57 - PubMed
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BR. et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013; 382: 339–352 - PubMed
-
- Herzog CA, Asinger RW, Berger AK. et al. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease. A clinical update from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int 2011; 80: 572–586 - PubMed