Efficacy and safety of 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 30281615
- PMCID: PMC6169865
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203479
Efficacy and safety of 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Although combination therapy with 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor (5ARI) and alpha-blocker is one of the standard interventions in symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), 5ARI monotherapy is seldom the focus of attention. Adverse events associated with 5ARI include depression and suicidal attempts in addition to persistent erectile dysfunction. The aim of this study is to update our knowledge of clinical efficacy and incidence of adverse events associated with 5ARI treatment in symptomatic BPH.
Methods and findings: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) from 1966 until March, 2017 was performed using database from PubMed, Cochrane Collaboration and Embase. A total of 23395 patients were included in this study and the inclusion criteria were: RCTs with 5ARI and placebo in symptomatic BPH patients. Parameters included prostate specific antigen (PSA), prostate volume (PV), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPPS), post-void residual urine (PVR), voiding symptoms of IPSS (voiding IPSS), maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax), and adverse events (AEs). A meta-analysis with meta-regression was performed for each effect size and adverse events, sensitivity analysis, cumulative analysis along with the analysis of ratio of means (ROM) in the placebo group. A total of 42 studies were included in this study for review, and a total of 37 studies were included in the meta-analysis, including a total of 23395 patients (treatment group: 11392, placebo group: 12003). The effect size of all variables except PVR showed a significant improvement following 5ARI treatment compared with placebo. However, the effect size of differences showed declining trend in PV, IPSS and Qmax according to recent years of publication. In ROM analysis, PV showed no significant increase in the placebo group, with a ROM of 1.00 (95% CI, 0.88, 1.14). The 5ARI treatment resulted in a significantly higher incidence of decreased libido (OR = 1.7; 95% CI, 1.36, 2.13), ejaculatory disorder (OR = 2.94; 95% CI, 2.15, 4.03), gynecomastia (OR = 2.32; 95% CI, 1.41, 3.83), and impotence (OR = 1.74; 95% CI, 1.32, 2.29). Our study has the following limitations: included studies were heterogeneous and direct comparison of efficacy between alpha blocker and 5ARI was not performed. Adverse events including depression or suicidal attempt could not be analyzed in this meta-analysis setting.
Conclusions: Although there was a significant clinical benefit of 5ARI monotherapy compared with placebo, the effective size was small. Moreover, the risk of adverse events including sexually related complications were high. Additional head-to-head studies are needed to re-evaluate the clinical efficacy of 5ARI compared with alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
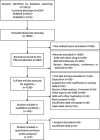

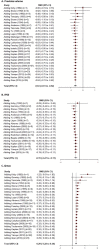
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of Finasteride (5 alpha-reductase inhibitor) monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia: A critical review of the literature.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020 Jan 13;91(4):205-210. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2019.4.205. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020. PMID: 31937082 Review.
-
Influence of baseline variables on changes in International Prostate Symptom Score after combined therapy with dutasteride plus tamsulosin or either monotherapy in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: 4-year results of the CombAT study.BJU Int. 2014 Apr;113(4):623-35. doi: 10.1111/bju.12500. Epub 2014 Jan 9. BJU Int. 2014. PMID: 24127818 Clinical Trial.
-
Sexual dysfunction in subjects treated with inhibitors of 5α-reductase for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis.Andrology. 2017 Jul;5(4):671-678. doi: 10.1111/andr.12353. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Andrology. 2017. PMID: 28453908 Review.
-
A prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel trial comparing the efficacy of α-blocker or 5α-reductase inhibitor withdrawal to continued combination therapy on the maintenance of lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia.Prostate. 2024 Mar;84(4):403-413. doi: 10.1002/pros.24663. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Prostate. 2024. PMID: 38149792 Clinical Trial.
-
A 5-year retrospective analysis of 5α-reductase inhibitors in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: finasteride has comparable urinary symptom efficacy and prostate volume reduction, but less sexual side effects and breast complications than dutasteride.Int J Clin Pract. 2012 Nov;66(11):1052-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2012.03010.x. Int J Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 23067029
Cited by
-
Suicidal risk associated with finasteride versus dutasteride among men treated for benign prostatic hyperplasia: nationwide cohort study.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 31;13(1):5308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32356-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37002313 Free PMC article.
-
Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2020 Dec 4;117(49):843-854. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2020.0843. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2020. PMID: 33593479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of alpha-blockers as monotherapy for benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 May 15;14(1):11116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61977-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38750153 Free PMC article.
-
Tadalafil Alone or in Combination with Tamsulosin for the Management for LUTS/BPH and ED.Curr Urol Rep. 2020 Oct 27;21(12):56. doi: 10.1007/s11934-020-01009-7. Curr Urol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33108544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Study of the Efficacy and Tolerability of Palmex® (Roystonea regia Lipid Extract), Saw Palmetto, Finasteride and Tamsulosin in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Urol Res Pract. 2025 Mar 7;50(5):302-309. doi: 10.5152/tud.2025.24067. Urol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40248996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McVary KT. BPH: epidemiology and comorbidities. Am J Manag Care. 2006;12(5 Suppl):S122–8. . - PubMed
-
- Yuan JQ, Mao C, Wong SY, Yang ZY, Fu XH, Dai XY, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Monodrug Therapies for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Associated With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Network Meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(27):e974 10.1097/MD.0000000000000974 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4504542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

