Transsynaptic Binding of Orphan Receptor GPR179 to Dystroglycan-Pikachurin Complex Is Essential for the Synaptic Organization of Photoreceptors
- PMID: 30282023
- PMCID: PMC6203450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.068
Transsynaptic Binding of Orphan Receptor GPR179 to Dystroglycan-Pikachurin Complex Is Essential for the Synaptic Organization of Photoreceptors
Abstract
Establishing synaptic contacts between neurons is paramount for nervous system function. This process involves transsynaptic interactions between a host of cell adhesion molecules that act in cooperation with the proteins of the extracellular matrix to specify unique physiological properties of individual synaptic connections. However, understanding of the molecular mechanisms that generate functional diversity in an input-specific fashion is limited. In this study, we identify that major components of the extracellular matrix proteins present in the synaptic cleft-members of the heparan sulfate proteoglycan (HSPG) family-associate with the GPR158/179 group of orphan receptors. Using the mammalian retina as a model system, we demonstrate that the HSPG member Pikachurin, released by photoreceptors, recruits a key post-synaptic signaling complex of downstream ON-bipolar neurons in coordination with the pre-synaptic dystroglycan glycoprotein complex. We further demonstrate that this transsynaptic assembly plays an essential role in synaptic transmission of photoreceptor signals.
Keywords: HSPG; ON-bipolar cells; heparan sulfate proteoglycan; orphan receptor; retina; ribbon synapse; synaptic specificity; synaptic transmission; transsynaptic interactions; vision.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

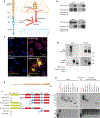
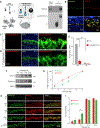
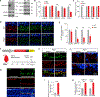
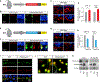
References
-
- Audo I, Bujakowska K, Orhan E, Poloschek CM, Defoort-Dhellemmes S, Drumare I, Kohl S, Luu TD, Lecompte O, Zrenner E, et al. (2012). Whole-exome sequencing identifies mutations in GPR179 leading to autosomal-recessive complete congenital stationary night blindness. Am. J.Hum. Genet 90, 321–330. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baeg GH, Lin X, Khare N, Baumgartner S, and Perrimon N (2001). Heparan sulfate proteoglycans are critical for the organization of the extracellular distribution of Wingless. Development 128, 87–94. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, and Marder E (2013). From the connectome to brain function.Nat. Methods 10, 483–490. - PubMed
-
- Bishop JR, Schuksz M, and Esko JD (2007). Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 446, 1030–1037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

