Elongation/Termination Factor Exchange Mediated by PP1 Phosphatase Orchestrates Transcription Termination
- PMID: 30282034
- PMCID: PMC6180485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.007
Elongation/Termination Factor Exchange Mediated by PP1 Phosphatase Orchestrates Transcription Termination
Abstract
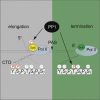
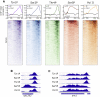
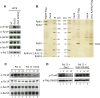
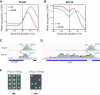
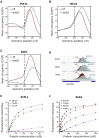
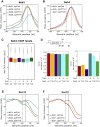
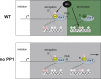
Termination of RNA polymerase II (Pol II) transcription is a key step that is important for 3' end formation of functional mRNA, mRNA release, and Pol II recycling. Even so, the underlying termination mechanism is not yet understood. Here, we demonstrate that the conserved and essential termination factor Seb1 is found on Pol II near the end of the RNA exit channel and the Rpb4/7 stalk. Furthermore, the Seb1 interaction surface with Pol II largely overlaps with that of the elongation factor Spt5. Notably, Seb1 co-transcriptional recruitment is dependent on Spt5 dephosphorylation by the conserved PP1 phosphatase Dis2, which also dephosphorylates threonine 4 within the Pol II heptad repeated C-terminal domain. We propose that Dis2 orchestrates the transition from elongation to termination phase during the transcription cycle by mediating elongation to termination factor exchange and dephosphorylation of Pol II C-terminal domain.
Keywords: C-terminal domain; CID; CTD; CTD interacting domain; CTD phosphorylation; PP1 phosphatase; RNA polymerase II; Spt5; transcription termination.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Cdk9-PP1 switch regulates the elongation-termination transition of RNA polymerase II.Nature. 2018 Jun;558(7710):460-464. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0214-z. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29899453 Free PMC article.
-
Separable functions of the fission yeast Spt5 carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) in capping enzyme binding and transcription elongation overlap with those of the RNA polymerase II CTD.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 May;30(10):2353-64. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00116-10. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20231361 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved protein Seb1 drives transcription termination by binding RNA polymerase II and nascent RNA.Nat Commun. 2017 Apr 3;8:14861. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14861. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28367989 Free PMC article.
-
Sub1 and RNAPII, until termination does them part.Transcription. 2018;9(1):52-60. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1333558. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Transcription. 2018. PMID: 28853990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simplicity is the Ultimate Sophistication-Crosstalk of Post-translational Modifications on the RNA Polymerase II.J Mol Biol. 2021 Jul 9;433(14):166912. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166912. Epub 2021 Mar 5. J Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33676925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The CDK9-SPT5 Axis in Control of Transcription Elongation by RNAPII.J Mol Biol. 2025 Jan 1;437(1):168746. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168746. Epub 2024 Aug 13. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39147127 Review.
-
Leishmania PNUTS discriminates between PP1 catalytic subunits through an RVxF-ΦΦ-F motif and polymorphisms in the PP1 C-tail and catalytic domain.J Biol Chem. 2023 Dec;299(12):105432. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105432. Epub 2023 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37926279 Free PMC article.
-
Defining gene ends: RNA polymerase II CTD threonine 4 phosphorylation marks transcription termination regions genome-wide.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jan 11;53(2):gkae1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae1240. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39718990 Free PMC article.
-
BRD4: a general regulator of transcription elongation.Transcription. 2022 Feb-Jun;13(1-3):70-81. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2108302. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Transcription. 2022. PMID: 36047906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic screen for suppression of transcriptional interference identifies a gain-of-function mutation in Pol2 termination factor Seb1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 17;118(33):e2108105118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2108105118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34389684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Austenaa L.M.I., Barozzi I., Simonatto M., Masella S., Della Chiara G., Ghisletti S., Curina A., de Wit E., Bouwman B.A.M., de Pretis S. Transcription of mammalian cis-regulatory elements is restrained by actively enforced early termination. Mol. Cell. 2015;60:460–474. - PubMed
-
- Baejen C., Andreani J., Torkler P., Battaglia S., Schwalb B., Lidschreiber M., Maier K.C., Boltendahl A., Rus P., Esslinger S. Genome-wide analysis of RNA polymerase II termination at protein-coding genes. Mol. Cell. 2017;66:38–49. - PubMed
-
- Bähler J., Wu J.-Q., Longtine M.S., Shah N.G., McKenzie A., 3rd, Steever A.B., Wach A., Philippsen P., Pringle J.R. Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast. 1998;14:943–951. - PubMed
-
- Bernecky C., Herzog F., Baumeister W., Plitzko J.M., Cramer P. Structure of transcribing mammalian RNA polymerase II. Nature. 2016;529:551–554. - PubMed
-
- Bird L.E. High throughput construction and small scale expression screening of multi-tag vectors in Escherichia coli. Methods. 2011;55:29–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

