A complete bioconversion cascade for dehalogenation and denitration by bacterial flavin-dependent enzymes
- PMID: 30282807
- PMCID: PMC6290146
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005538
A complete bioconversion cascade for dehalogenation and denitration by bacterial flavin-dependent enzymes
Abstract
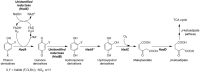
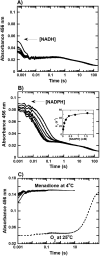
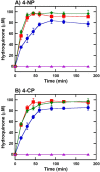
Halogenated phenol and nitrophenols are toxic compounds that are widely accumulated in the environment. Enzymes in the had operon from the bacterium Ralstonia pickettii DTP0602 have the potential for application as biocatalysts in the degradation of many of these toxic chemicals. HadA monooxygenase previously was identified as a two-component reduced FAD (FADH-)-utilizing monooxygenase with dual activities of dehalogenation and denitration. However, the partner enzymes of HadA, that is, the flavin reductase and quinone reductase that provide the FADH- for HadA and reduce quinone to hydroquinone, remain to be identified. In this report, we overexpressed and purified the flavin reductases, HadB and HadX, to investigate their functional and catalytic properties. Our results indicated that HadB is an FMN-dependent quinone reductase that converts the quinone products from HadA to hydroquinone compounds that are more stable and can be assimilated by downstream enzymes in the pathway. Transient kinetics indicated that HadB prefers NADH and menadione as the electron donor and acceptor, respectively. We found that HadX is an FAD-bound flavin reductase, which can generate FADH- for HadA to catalyze dehalogenation or denitration reactions. Thermodynamic and transient kinetic experiments revealed that HadX prefers to bind FAD over FADH- and that HadX can transfer FADH- from HadX to HadA via free diffusion. Moreover, HadX rapidly catalyzed NADH-mediated reduction of flavin and provided the FADH- for a monooxygenase of a different system. Combination of all three flavin-dependent enzymes, i.e. HadA/HadB/HadX, reconstituted an effective dehalogenation and denitration cascade, which may be useful for future bioremediation applications.
Keywords: bioremediation; biotechnology; enzyme kinetics; enzyme mechanism; flavin; flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD); flavoenzyme; halogenated phenol; nitrophenol; reductase.
© 2018 Pimviriyakul and Chaiyen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

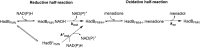







References
-
- Igbinosa E. O., Odjadjare E. E., Chigor V. N., Igbinosa I. H., Emoghene A. O., Ekhaise F. O., Igiehon N. O., and Idemudia O. G. (2013) Toxicological profile of chlorophenols and their derivatives in the environment: the public health perspective. Scientific World J. 2013, 1–11 10.1155/2013/460215 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pera-Titus M., Garcia-Molina V., Banos M. A., Gimenez J., and Esplugas S. (2004) Degradation of chlorophenols by means of advanced oxidation processes: a general review. Appl. Catal. B-Environ 47, 219–256 10.1016/j.apcatb.2003.09.010 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

