Endo-fucoidan hydrolases from glycoside hydrolase family 107 (GH107) display structural and mechanistic similarities to α-l-fucosidases from GH29
- PMID: 30282808
- PMCID: PMC6254363
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005134
Endo-fucoidan hydrolases from glycoside hydrolase family 107 (GH107) display structural and mechanistic similarities to α-l-fucosidases from GH29
Abstract
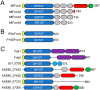
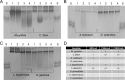
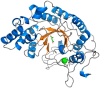
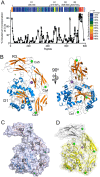
Fucoidans are chemically complex and highly heterogeneous sulfated marine fucans from brown macro algae. Possessing a variety of physicochemical and biological activities, fucoidans are used as gelling and thickening agents in the food industry and have anticoagulant, antiviral, antitumor, antibacterial, and immune activities. Although fucoidan-depolymerizing enzymes have been identified, the molecular basis of their activity on these chemically complex polysaccharides remains largely uninvestigated. In this study, we focused on three glycoside hydrolase family 107 (GH107) enzymes: MfFcnA and two newly identified members, P5AFcnA and P19DFcnA, from a bacterial species of the genus Psychromonas Using carbohydrate-PAGE, we show that P5AFcnA and P19DFcnA are active on fucoidans that differ from those depolymerized by MfFcnA, revealing differential substrate specificity within the GH107 family. Using a combination of X-ray crystallography and NMR analyses, we further show that GH107 family enzymes share features of their structures and catalytic mechanisms with GH29 α-l-fucosidases. However, we found that GH107 enzymes have the distinction of utilizing a histidine side chain as the proposed acid/base catalyst in its retaining mechanism. Further interpretation of the structural data indicated that the active-site architectures within this family are highly variable, likely reflecting the specificity of GH107 enzymes for different fucoidan substructures. Together, these findings begin to illuminate the molecular details underpinning the biological processing of fucoidans.
Keywords: X-ray crystallography; enzyme; enzyme catalysis; enzyme mechanism; glycoside hydrolase; polysaccharide.
© 2018 Vickers et al.
Conflict of interest statement
C. V., K. A., O. S.-A., and A. B. B. are named inventors on a patent application to protect the intellectual property surrounding the field of use for these enzymes. They have assigned their rights to ARC Medical Devices Inc. and have no current or future financial interest in the patent application/patent
Figures



References
-
- Angstwurm K., Weber J. R., Segert A., Bürger W., Weih M., Freyer D., Einhäupl K. M., and Dirnagl U. (1995) Fucoidin, a polysaccharide inhibiting leukocyte rolling, attenuates inflammatory responses in experimental pneumococcal meningitis in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 191, 1–4 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11541-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Preobrazhenskaya M. E., Berman A. E., Mikhailov V. I., Ushakova N. A., Mazurov A. V., Semenov A. V., Usov A. I., Nifant'ev N. E., and Bovin N. V. (1997) Fucoidan inhibits leukocyte recruitment in a model peritonial inflammation in rat and blocks interaction of P-selectin with its carbohydrate ligand. IUBMB Life 43, 443–451 10.1080/15216549700204231 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

