Combining Microbubble Contrast Agent with Pulsed-Laser Irradiation for Transdermal Drug Delivery
- PMID: 30282960
- PMCID: PMC6321619
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10040175
Combining Microbubble Contrast Agent with Pulsed-Laser Irradiation for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Abstract
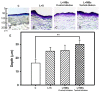
The optodynamic process of laser-induced microbubble (MB) cavitation in liquids is utilized in various medical applications. However, how incident laser radiation interacts with MBs as an ultrasound contrast agent is rarely estimated when the liquid already contains stable MBs. The present study investigated the efficacy of the laser-mediated cavitation of albumin-shelled MBs in enhancing transdermal drug delivery. Different types and conditions of laser-mediated inertial cavitation of MBs were first evaluated. A CO₂ fractional pulsed laser was selected for combining with MBs in the in vitro and in vivo experiments. The in vitro skin penetration by β-arbutin after 2 h was 2 times greater in the group combining a laser with MBs than in the control group. In small-animal experiments, the whitening effect on the skin of C57BL/6J mice in the group combining a laser with MBs on the skin plus penetrating β-arbutin increased (significantly) by 48.0% at day 11 and 50.0% at day 14, and then tended to stabilize for the remainder of the 20-day experimental period. The present results indicate that combining a CO₂ laser with albumin-shelled MBs can increase skin permeability so as to enhance the delivery of β-arbutin to inhibit melanogenesis in mice without damaging the skin.
Keywords: arbutin; cavitation; laser; transdermal; ultrasound contrast agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Dalecki D. Biological Effects of Microbubble-Based Ultrasound Contrast Agents. In: Emilio Q., editor. Contrast Media in Ultrasonography: Basic Principles and Clinical Applications. Springer-Verlag; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2005. pp. 77–85.
-
- Li P., Cao L.Q., Dou C.Y., Armstrong W.F., Miller D. Impact of myocardial contrast echocardiography on vascular permeability: An in vivo dose response study of delivery mode, pressure amplitude and contrast dose. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003;29:1341–1349. doi: 10.1016/S0301-5629(03)00988-8. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

