Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
- PMID: 30282987
- PMCID: PMC6170409
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06183-4
Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 14;9(1):4851. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07398-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30429483 Free PMC article.
-
Author Correction: Bi-directional cell-pericellular matrix interactions direct stem cell fate.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 18;9(1):5419. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07843-1. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30560926 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Modifiable hydrogels have revealed tremendous insight into how physical characteristics of cells' 3D environment drive stem cell lineage specification. However, in native tissues, cells do not passively receive signals from their niche. Instead they actively probe and modify their pericellular space to suit their needs, yet the dynamics of cells' reciprocal interactions with their pericellular environment when encapsulated within hydrogels remains relatively unexplored. Here, we show that human bone marrow stromal cells (hMSC) encapsulated within hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels modify their surroundings by synthesizing, secreting and arranging proteins pericellularly or by degrading the hydrogel. hMSC's interactions with this local environment have a role in regulating hMSC fate, with a secreted proteinaceous pericellular matrix associated with adipogenesis, and degradation with osteogenesis. Our observations suggest that hMSC participate in a bi-directional interplay between the properties of their 3D milieu and their own secreted pericellular matrix, and that this combination of interactions drives fate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
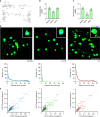
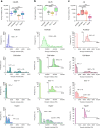

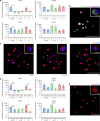
Similar articles
-
Neighboring cells override 3D hydrogel matrix cues to drive human MSC quiescence.Biomaterials. 2018 Sep;176:13-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.05.032. Epub 2018 May 22. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29852376 Free PMC article.
-
Heparin-hyaluronic acid hydrogel in support of cellular activities of 3D encapsulated adipose derived stem cells.Acta Biomater. 2017 Feb;49:284-295. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27919839
-
Vascular differentiation of bone marrow stem cells is directed by a tunable three-dimensional matrix.Acta Biomater. 2010 Sep;6(9):3395-403. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2010.03.019. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Acta Biomater. 2010. PMID: 20302976
-
Effects of biophysical cues of 3D hydrogels on mesenchymal stem cells differentiation.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Apr;236(4):2268-2275. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30042. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 32885847 Review.
-
Growth factor binding to the pericellular matrix and its importance in tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007 Nov 10;59(13):1366-81. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2007.08.015. Epub 2007 Aug 16. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007. PMID: 17916397 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the ECM Microenvironment to Ameliorate Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy in Chronic Lung Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 15;12:645558. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645558. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34040521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methine initiated polypropylene-based disposable face masks aging validated by micromechanical properties loss of atomic force microscopy.J Hazard Mater. 2023 Jan 5;441:129831. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129831. Epub 2022 Aug 24. J Hazard Mater. 2023. PMID: 36084457 Free PMC article.
-
Egr1 is a 3D matrix-specific mediator of mechanosensitive stem cell lineage commitment.Sci Adv. 2022 Apr 15;8(15):eabm4646. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abm4646. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35427160 Free PMC article.
-
Human Adventitial Fibroblast Phenotype Depends on the Progression of Changes in Substrate Stiffness.Adv Healthc Mater. 2020 Apr;9(8):e1901593. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201901593. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020. PMID: 32105417 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that TNF-β suppresses osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and resveratrol reverses it through modulation of NF-κB, Sirt1 and Runx2.Cell Tissue Res. 2020 Jul;381(1):83-98. doi: 10.1007/s00441-020-03188-8. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2020. PMID: 32140928
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

