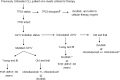
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment algorithm 2018
- PMID: 30283014
- PMCID: PMC6170426
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-018-0131-2
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment algorithm 2018
Abstract
The treatment landscape for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) has changed considerably with the introduction of very effective oral targeted therapies (such as ibrutinib, idelalisib, and venetoclax), and next-generation anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies (such as obinutuzumab). These agents lead to improved outcomes in CLL, even among patients with high-risk features, such as del17p13 or TP53 mutation and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV) genes. Each of these treatments is associated with a unique toxicity profile; in the absence of randomized data, the choice of one type of treatment over another depends on the co-morbidities of the patient. Chemoimmunotherapy still plays an important role in the management of previously untreated CLL patients, particularly among young fit patients who have standard risk FISH profile and mutated IGHV genes. Richter's transformation of CLL remains a difficult complication to treat, although therapy with programmed death 1 inhibitors such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab has shown impressive responses in a subset of patients. Our ability to risk stratify CLL patients continues to evolve; the CLL-International Prognostic Index (CLL-IPI) is the best validated tool in predicting time to first therapy among previously untreated patients. This review summarizes the current approach to risk stratification and management of CLL patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Research funding has been provided to the institution from Pharmacyclics, MorphoSyS, Janssen, AbbVie, and AstraZeneca for clinical studies in which Sameer A. Parikh is a principal investigator. Sameer A. Parikh has also participated in Advisory Board meetings of Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, Gilead, and AbbVie (he was not personally compensated for his participation).
Figures


References
-
- Swerdlow, S. et al. (eds) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th edn (World Health Organization, 2008), Lyon, France.
-
- Parikh Sameer A., Chaffee Kari G., Larson Melissa C., Hampel Paul J., Call Timothy G., Ding Wei, Kenderian Saad S., Leis Jose F., Chanan-Khan Asher A., Conte Michael J., Bowen Deborah, Schwager Susan M., Slager Susan L., Hanson Curtis A., Kay Neil E., Shanafelt Tait D. Outcomes of a large cohort of individuals with clinically ascertained high-count monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis. Haematologica. 2018;103(6):e237–e240. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.183194. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hallek Michael, Cheson Bruce D., Catovsky Daniel, Caligaris-Cappio Federico, Dighiero Guillermo, Döhner Hartmut, Hillmen Peter, Keating Michael, Montserrat Emili, Chiorazzi Nicholas, Stilgenbauer Stephan, Rai Kanti R., Byrd John C., Eichhorst Barbara, O’Brien Susan, Robak Tadeusz, Seymour John F., Kipps Thomas J. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood. 2018;131(25):2745–2760. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-09-806398. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

