Tobacco smoking and the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies
- PMID: 30283044
- PMCID: PMC6170425
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-32100-2
Tobacco smoking and the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies
Abstract
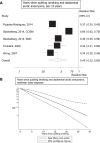
Several studies have found that smoking increases the risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm, however, the strength of the association has differed between studies and data from cohort studies have not yet been summarized. A systematic review and meta-analysis was therefore conducted to clarify this association. We searched PubMed and Embase databases up to May 2nd 2018. A random effects model was used to estimate summary relative risks (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Twenty three prospective studies were included. Comparing current, former and ever smokers with never smokers the summary RRs were 4.87 (95% CI: 3.93-6.02, I2 = 92%, n = 20), 2.10 (95% CI: 1.76-2.50, I2 = 71%, n = 15) and 3.28 (95% CI: 2.60-4.15, I2 = 96%, n = 18), respectively. The summary RR was 1.87 (95% CI: 1.45-2.40, I2 = 97%) per 10 cigarettes per day, 1.78 (95% CI: 1.54-2.06, I2 = 83%) per 10 pack-years was and 0.45 (95% CI: 0.32-0.63, I2 = 92.3%) per 10 years of smoking cessation. There was evidence of nonlinearity for cigarettes per day and pack-years (pnonlinearity < 0.0001 and pnonlinearity = 0.02, respectively), but not for smoking cessation, pnonlinearity = 0.85. Among smokers who quit, the RR was similar to that of never smokers by 25 years of smoking cessation. These findings confirm a strong association between smoking and the risk of developing abdominal aortic aneurysms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Johnston KW, et al. Suggested standards for reporting on arterial aneurysms. Subcommittee on Reporting Standards for Arterial Aneurysms, Ad Hoc Committee on Reporting Standards, Society for Vascular Surgery and North American Chapter, International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery. J. Vasc. Surg. 1991;13:452–458. doi: 10.1067/mva.1991.26737. - DOI - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1459–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD 2015 DALYs and HALE Collaborators Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 315 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE), 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1603–1658. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31460-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

