A mean score method for sensitivity analysis to departures from the missing at random assumption in randomised trials
- PMID: 30283213
- PMCID: PMC6166859
- DOI: 10.5705/ss.202016.0308
A mean score method for sensitivity analysis to departures from the missing at random assumption in randomised trials
Abstract
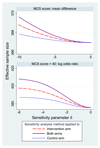
Most analyses of randomised trials with incomplete outcomes make untestable assumptions and should therefore be subjected to sensitivity analyses. However, methods for sensitivity analyses are not widely used. We propose a mean score approach for exploring global sensitivity to departures from missing at random or other assumptions about incomplete outcome data in a randomised trial. We assume a single outcome analysed under a generalised linear model. One or more sensitivity parameters, specified by the user, measure the degree of departure from missing at random in a pattern mixture model. Advantages of our method are that its sensitivity parameters are relatively easy to interpret and so can be elicited from subject matter experts; it is fast and non-stochastic; and its point estimate, standard error and confidence interval agree perfectly with standard methods when particular values of the sensitivity parameters make those standard methods appropriate. We illustrate the method using data from a mental health trial.
Keywords: Intention-to-treat analysis; Longitudinal data analysis; Mean score; Missing data; Randomised trials; Sensitivity analysis.
Figures
References
-
- Carpenter JR, Kenward MG, White IR. Sensitivity analysis after multiple imputation under missing at random: a weighting approach. Statistical Methods in Medical Research. 2007;16(3):259–275. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter JR, Roger JH, Kenward MG. Analysis of longitudinal trials with protocol deviation: a framework for relevant, accessible assumptions, and inference via multiple imputation. Journal of Biopharmaceutical Statistics. 2013;23(3):1352–71. - PubMed
-
- Daniels MJ, Hogan JW. Reparameterizing the Pattern Mixture Model for Sensitivity Analyses Under Informative Dropout. Biometrics. 2000;56(4):1241–1248. - PubMed
-
- Diggle P, Kenward MG. Informative drop-out in longitudinal data analysis. Applied Statistics. 1994;43(1):49–93.
-
- Dufouil C, Brayne C, Clayton D. Analysis of longitudinal studies with death and drop-out: a case study. Statistics in Medicine. 2004;23(14):2215–2226. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources