Strong hybrid male incompatibilities impede the spread of a selfish chromosome between populations of a fly
- PMID: 30283674
- PMCID: PMC6121854
- DOI: 10.1002/evl3.55
Strong hybrid male incompatibilities impede the spread of a selfish chromosome between populations of a fly
Abstract
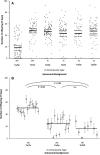
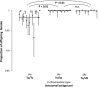
Meiotically driving sex chromosomes manipulate gametogenesis to increase their transmission at a cost to the rest of the genome. The intragenomic conflicts they produce have major impacts on the ecology and evolution of their host species. However, their ecological dynamics remain poorly understood. Simple population genetic models predict meiotic drivers will rapidly reach fixation in populations and spread across landscapes. In contrast, natural populations commonly show spatial variation in the frequency of drivers, with drive present in clines or mosaics across species ranges. For example, Drosophila subobscura harbors a sex ratio distorting drive chromosome (SRs) at 15-25% frequency in North Africa, present at less than 2% frequency in adjacent southern Spain, and absent in other European populations. Here, we investigate the forces preventing the spread of the driver northward. We show that SRs has remained at a constant frequency in North Africa, and failed to spread in Spain. We find strong evidence that spread is impeded by genetic incompatibility between SRs and Spanish autosomal backgrounds. When we cross SRs from North Africa onto Spanish genetic backgrounds we observe strong incompatibilities specific to hybrids bearing SRs. The incompatibilities increase in severity in F2 male hybrids, leading to almost complete infertility. We find no evidence supporting an alternative hypothesis, that there is resistance to drive in Spanish populations. We conclude that the source of the stepped frequency variation is genetic incompatibility between the SRs chromosome and the genetic backgrounds of the adjacent population, preventing SRs spreading northward. The low frequency of SRs in South Spain is consistent with recurrent gene flow across the Strait of Gibraltar combined with selection against the SRs element through genetic incompatibility. This demonstrates that incompatibilities between drive chromosomes and naïve populations can prevent the spread of drive between populations, at a continental scale.
Keywords: Compatibility; Drosophila subobscura; X chromosome meiotic drive; segregation‐distortion; selfish genetic elements; suppression.
Figures



References
-
- Babcock, C. S. , and Anderson W. W.. 1996. Molecular evolution of the sex‐ratio inversion complex in Drosophila pseudoobscura: analysis of the esterase‐5 gene region. Mol. Biol. Evol. 13:297–308. - PubMed
-
- Bastide, H. , Cazemajor M., Ogereau D., Derome N., Hospital F., and Montchamp‐Moreau C.. 2011. Rapid rise and fall of selfish sex‐ratio X chromosomes in Drosophila simulans: spatiotemporal analysis of phenotypic and molecular data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28:2461–2470. - PubMed
-
- Bryant, S. H. , Beckenbach A. T., and Cobbs G. A.. 1982. Sex‐ratio trait, sex composition, and relative abundance in Drosophila pseudoobscura . Evolution 36:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Burt, A. , and Trivers R.. 2006. Genes in conflict: the biology of selfish genetic elements. Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, MA.
-
- Cobbs, G. 1992. Sex chromosome loss induced by the “sex‐ratio” trait in Drosophila pseudoobscura males. J. Heredity 83:81–84. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

