Indirect Calorimetry: History, Technology, and Application
- PMID: 30283765
- PMCID: PMC6157446
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2018.00257
Indirect Calorimetry: History, Technology, and Application
Abstract
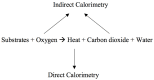
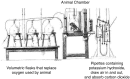
Measurement of energy expenditure is important in order to determine basal metabolic rate and inform energy prescription provided. Indirect calorimetry is the reference standard and clinically recommended means to measure energy expenditure. This article reviews the historical development, technical, and logistic challenges of indirect calorimetry measurement, and provides case examples for practicing clinicians. Formulae to estimate energy expenditure are highly inaccurate and reinforce the role of the indirect calorimetry and the importance of understanding the strength and limitation of the method and its application.
Keywords: calorimetry; closed-circuit calorimetry; critically ill children; energy expenditure; energy metabolism; indirect calorimetry; open-circuit calorimetry.
Figures
References
-
- Mehta NM, Skillman HE, Irving SY, Coss-Bu JA, Vermilyea S, Farrington EA, et al. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the pediatric critically ill patient: society of critical care medicine and american society for parenteral and enteral nutrition. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2017) 18:675–715. 10.1177/0148607117711387 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

