Psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents
- PMID: 30284240
- PMCID: PMC6517234
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005179.pub4
Psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents
Abstract
Background: This is the second update of a Cochrane Review (Issue 4, 2006). Pain and distress from needle-related procedures are common during childhood and can be reduced through use of psychological interventions (cognitive or behavioral strategies, or both). Our first review update (Issue 10, 2013) showed efficacy of distraction and hypnosis for needle-related pain and distress in children and adolescents.
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents.
Search methods: We searched six electronic databases for relevant trials: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL); MEDLINE; PsycINFO; Embase; Web of Science (ISI Web of Knowledge); and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL). We sent requests for additional studies to pediatric pain and child health electronic listservs. We also searched registries for relevant completed trials: clinicaltrials.gov; and World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (www.who.int.trialsearch). We conducted searches up to September 2017 to identify records published since the last review update in 2013.
Selection criteria: We included peer-reviewed published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with at least five participants per study arm, comparing a psychological intervention with a control or comparison group. Trials involved children aged two to 19 years undergoing any needle-related medical procedure.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors extracted data and assessed risks of bias using the Cochrane 'Risk of bias' tool. We examined pain and distress assessed by child self-report, observer global report, and behavioral measurement (primary outcomes). We also examined any reported physiological outcomes and adverse events (secondary outcomes). We used meta-analysis to assess the efficacy of identified psychological interventions relative to a comparator (i.e. no treatment, other active treatment, treatment as usual, or waitlist) for each outcome separately. We used Review Manager 5 software to compute standardized mean differences (SMDs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and GRADE to assess the quality of the evidence.
Main results: We included 59 trials (20 new for this update) with 5550 participants. Needle procedures primarily included venipuncture, intravenous insertion, and vaccine injections. Studies included children aged two to 19 years, with few trials focused on adolescents. The most common psychological interventions were distraction (n = 32), combined cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT; n = 18), and hypnosis (n = 8). Preparation/information (n = 4), breathing (n = 4), suggestion (n = 3), and memory alteration (n = 1) were also included. Control groups were often 'standard care', which varied across studies. Across all studies, 'Risk of bias' scores indicated several domains at high or unclear risk, most notably allocation concealment, blinding of participants and outcome assessment, and selective reporting. We downgraded the quality of evidence largely due to serious study limitations, inconsistency, and imprecision.Very low- to low-quality evidence supported the efficacy of distraction for self-reported pain (n = 30, 2802 participants; SMD -0.56, 95% CI -0.78 to -0.33) and distress (n = 4, 426 participants; SMD -0.82, 95% CI -1.45 to -0.18), observer-reported pain (n = 11, 1512 participants; SMD -0.62, 95% CI -1.00 to -0.23) and distress (n = 5, 1067 participants; SMD -0.72, 95% CI -1.41 to -0.03), and behavioral distress (n = 7, 500 participants; SMD -0.44, 95% CI -0.84 to -0.04). Distraction was not efficacious for behavioral pain (n = 4, 309 participants; SMD -0.33, 95% CI -0.69 to 0.03). Very low-quality evidence indicated hypnosis was efficacious for reducing self-reported pain (n = 5, 176 participants; SMD -1.40, 95% CI -2.32 to -0.48) and distress (n = 5, 176 participants; SMD -2.53, 95% CI -3.93 to -1.12), and behavioral distress (n = 6, 193 participants; SMD -1.15, 95% CI -1.76 to -0.53), but not behavioral pain (n = 2, 69 participants; SMD -0.38, 95% CI -1.57 to 0.81). No studies assessed hypnosis for observer-reported pain and only one study assessed observer-reported distress. Very low- to low-quality evidence supported the efficacy of combined CBT for observer-reported pain (n = 4, 385 participants; SMD -0.52, 95% CI -0.73 to -0.30) and behavioral distress (n = 11, 1105 participants; SMD -0.40, 95% CI -0.67 to -0.14), but not self-reported pain (n = 14, 1359 participants; SMD -0.27, 95% CI -0.58 to 0.03), self-reported distress (n = 6, 234 participants; SMD -0.26, 95% CI -0.56 to 0.04), observer-reported distress (n = 6, 765 participants; SMD 0.08, 95% CI -0.34 to 0.50), or behavioral pain (n = 2, 95 participants; SMD -0.65, 95% CI -2.36 to 1.06). Very low-quality evidence showed efficacy of breathing interventions for self-reported pain (n = 4, 298 participants; SMD -1.04, 95% CI -1.86 to -0.22), but there were too few studies for meta-analysis of other outcomes. Very low-quality evidence revealed no effect for preparation/information (n = 4, 313 participants) or suggestion (n = 3, 218 participants) for any pain or distress outcome. Given only a single trial, we could draw no conclusions about memory alteration. Adverse events of respiratory difficulties were only reported in one breathing intervention.
Authors' conclusions: We identified evidence supporting the efficacy of distraction, hypnosis, combined CBT, and breathing interventions for reducing children's needle-related pain or distress, or both. Support for the efficacy of combined CBT and breathing interventions is new from our last review update due to the availability of new evidence. The quality of trials and overall evidence remains low to very low, underscoring the need for improved methodological rigor and trial reporting. Despite low-quality evidence, the potential benefits of reduced pain or distress or both support the evidence in favor of using these interventions in clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
KA Birnie: none known. Dr. Birnie is a registered psychologist and works with children, adolescents, adults, and their families with pain and other acute and chronic illness.
M Noel: none known. Dr. Noel is a registered psychologist and works with children and adolescents with acute and chronic illness, and their families.
CT Chambers: none known. Dr. Chambers is a registered psychologist and works with children and their families with pain and other acute and chronic illness.
LS Uman: none known. Dr. Uman is a registered psychologist who works with youth and their families to address complex pain, other health‐related issues, and a variety of mental health concerns.
JA Parker: none known.
Figures





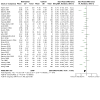


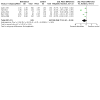





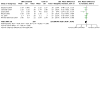



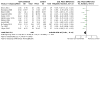








Update of
-
Psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 10;(10):CD005179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005179.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 04;10:CD005179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005179.pub4. PMID: 24108531 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Aydin 2017 {published data only}
-
- Aydin D, Sahiner NC. Effects of music therapy and distraction cards on pain relief during phlebotomy in children. Applied Nursing Research 2017;33:164-8. - PubMed
Balan 2009 {published data only}
-
- Balan R, Bavdekar SB, Jadhav S. Can Indian classical instrumental music reduce pain felt during venepuncture? Indian Journal of Pediatrics 2009;76(5):469-73. - PubMed
Bellieni 2006 {published data only}
Beran 2013 {published data only}
-
- Beran TN, Ramirez-Serrano A, Vanderkooi OG, Kuhn S. Reducing children’s pain and distress towards flu vaccinations: A novel and effective application of humanoid robotics. Vaccine 2013;31(25):2772– 7. - PubMed
Bisignano 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bisignano A, Bush JP. Distress in pediatric hematology-oncology patients undergoing intravenous procedures: Evaluation of a CD-ROM intervention. Children's Health Care 2006;35(1):61-74.
Blount 1992 {published data only}
-
- Blount RL, Bachanas PJ, Powers SW, Cotter MC, Franklin A, Chaplin W, et al. Training children to cope and parents to coach them during routine immunizations: Effects on child, parent, and staff behaviors. Behavior Therapy 1992;23:689-705.
Caprilli 2007 {published data only}
-
- Caprilli S, Anastasi F, Grotto RP, Scollo Abeti M, Messeri A. Interactive music as a treatment for pain and stress in children during venipuncture: A randomized prospective study. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 2007;28(5):399-403. - PubMed
Cassidy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cassidy K-R, Reid GJ, McGrath PJ, Finley GA, Smith DJ, Morley C, et al. Watch needle, watch TV: Audiovisual distraction in preschool immunization. American Academy of Pain Medicine 2002;3(2):108-18. - PubMed
Cavender 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cavender K, Goff MD, Hollon EC, Guzzetta CE. Parent's positioning and distracting children during venipuncture. Journal of Holistic Nursing 2004;22(1):32-56. - PubMed
Chen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chen E, Zeltzer LK, Craske MG, Katz ER. Alteration of memory in the reduction of children's distress during repeated aversive medical procedures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1999;67(4):481-90. - PubMed
Cohen 2015 {published data only}
Crevatin 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Crevatin F, Cozzi G, Braido E, Bertossa G, Rizzitelli P, Lionetti D, et al. Hand-held computers can help to distract children undergoing painful venipuncture procedures. Acta Paediatrica 2016;105(8):930-4. - PubMed
Ebrahimpour 2015 {published data only}
Eland 1981 {published data only}
-
- Eland JM. Minimizing pain associated with prekindergarten intramuscular injections. Issues in Comprehensive Pediatric Nursing 1981;5(5-6):361-72. - PubMed
Fanurik 2000 {published data only}
-
- Fanurik D, Koh JL, Schmitz ML. Distraction techniques combined with EMLA: Effects of IV insertion pain and distress in children. Children's Health Care 2000;29(2):87-101.
Fowler‐Kerry 1987 {published data only}
-
- Fowler-Kerry S, Lander JR. Management of injection pain in children. Pain 1987;30(2):169-75. - PubMed
Gold 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gold JI, Kim SH, Kant AJ, Joseph MH, Rizzo A. Effectiveness of virtual reality for pediatric pain distraction during IV placement. Cyberpsychology and Behavior 2006;9(2):207-12. - PubMed
Gonzalez 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez JC, Routh DK. Effects of maternal distraction versus reassurance on children's reactions to injections. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1993;18(5):593-604. - PubMed
Goodenough 1997 {published data only}
-
- Goodenough B, Kampel L, Champion GD, Laubreaux L, Nicholas MK, Ziegler JB, et al. An investigation of the placebo effect and age-related factors in the report of needle pain from venipuncture in children. Pain 1997;72(3):383-91. - PubMed
Gupta 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gupta D, Agarwal A, Dhiraaj S, Tandon M, Kumar M, Singh RS, et al. An evaluation of efficacy of balloon inflation on venous cannulation pain in children: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006;102(5):1372-5. - PubMed
Harrison 1991 {published data only}
-
- Harrison A. Preparing children for venous blood sampling. Pain 1991;45(3):299-306. - PubMed
Huet 2011 {published data only}
-
- Huet A, Lucas-Polomeni MM, Robert JC, Sixou JL, Wodey E. Hypnosis and dental anesthesia in children: A prospective controlled study. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 2011;59(4):424-40. - PubMed
Inal 2012 {published data only}
-
- Inal S, Kelleci M. Distracting children during blood draw: Looking through distraction cards is effective in pain relief of children during blood draw. International Journal of Nursing Practice 2012;18(2):210-9. - PubMed
Jeffs 2007 {published data only}
-
- Jeffs DA. A pilot study of distraction for adolescents during allergy testing. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing 2007;12(3):170-85. - PubMed
Kamath 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kamath PS. A novel distraction technique for pain management during local anesthesia administration in pediatric patients. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 2013;38(1):45-8. - PubMed
Katz 1987 {published data only}
-
- Katz ER, Kellerman J, Ellenberg L. Hypnosis in the reduction of acute pain and distress in children with cancer. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1987;12(3):379-94. - PubMed
Kleiber 2001 {published data only}
-
- Kleiber C, Craft-Rosenberg M, Harper DC. Parents as distraction coaches during IV insertion: A randomized study. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2001;22(4):851-61. - PubMed
Kristjansdottir 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kristjansdottir O, Kristjansdottir G. Randomized clinical trial of musical distraction with and without headphones for adolescents' immunization pain. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences 2011;25(1):19-26. - PubMed
Kuttner 1987 {published data only}
-
- Kuttner L. Favorite stories: A hypnotic pain-reduction technique for children in acute pain. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 1988;30(4):289-95. - PubMed
Liossi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Liossi C, Hatira P. Clinical hypnosis versus cognitive behavioral training for pain management with pediatric cancer patients undergoing bone marrow aspirations. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 1999;47(2):104-16. - PubMed
Liossi 2003 {published data only}
-
- Liossi C, Hatira P. Clinical hypnosis in the alleviation of procedure-related pain in pediatric oncology patients. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis 2003;51(1):4-28. - PubMed
Liossi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Liossi C, White P, Hatira P. Randomized clinical trial of local anesthetic versus a combination of local anesthetic with self-hypnosis in the management of pediatric procedure-related pain. Health Psychology 2006;25(3):307-15. - PubMed
Liossi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Liossi C, White P, Hatira P. A randomized clinical trial of a brief hypnosis intervention to control venepuncture-related pain of paediatric cancer patients. Pain 2009;142(3):255-63. - PubMed
Luthy 2013 {published data only}
-
- Luthy KE, Beckstrand RL, Pulsipher A. Evaluation of methods to relieve parental perceptions of vaccine-associated pain and anxiety in children: a pilot study. Journal of Pediatric Health Care 2013;27(5):351-8. - PubMed
McCarthy 2010 {published data only}
Meiri 2016 {published data only}
-
- Meiri N, Ankri A, Hamad-Saied M, Konopnicki M, Pillar G. The effect of medical clowning on reducing pain, crying, and anxiety in children aged 2–10 years old undergoing venous blood drawing—a randomized controlled study. European Journal of Pediatrics 2016;175(3):373–9. - PubMed
Miguez‐Navarro 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Miguez-Navarro C, Guerrero-Marquez G. Video-distraction system to reduce anxiety and pain in children subjected to venipuncture in pediatric emergencies. Pediatric Emergency Care and Medicine: Open Access 2016;1(1):1-8.
Miller 2016 {published data only}
-
- Miller K, Tan X, Hobson AD, Khan A, Ziviani J, O'Brien E, et al. A prospective randomized controlled trial of nonpharmacological pain management during intravenous cannulation in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatric Emergency Care 2016;32(7):444-51. - PubMed
Minute 2012 {published data only}
-
- Minute M, Badina L, Cont G, Montico M, Ronfani L, Barbi E, et al. Videogame playing as distraction technique in course of venipuncture [Giocare con i videogiochi come distrazione attiva in corso di venipuntura]. Pediatria Medica e Chirurgica (Medical and Surgical Pediatrics) 2012;34(2):77-83. - PubMed
Mutlu 2015a {published data only}
-
- Mutlu B, Balcı S. Effects of balloon inflation and cough trick methods on easing pain in children during the drawing of venous blood samples: a randomized controlled trial. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing 2015;20(3):178-86. - PubMed
Nguyen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nguyen TN, Nilsson S, Hellstrom A-L, Bengtson A. Music therapy to reduce pain and anxiety in children with cancer undergoing lumbar puncture: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing 2010;27(3):146-55. - PubMed
Nilsson 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nilsson S, Forsner M, Finnström B, Mörelius C. Relaxation and guided imagery do not reduce stress, pain and unpleasantness for 11- to 12-year-old girls during vaccinations. Acta Paediatrica 2015;104(7):724–9. - PubMed
Noguchi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Noguchi LK. The effect of music versus nonmusic on behavioral signs of distress and self-report of pain in pediatric injection patients. Journal of Music Therapy 2006;43(1):16-38. - PubMed
Oliveira 2017 {published data only}
-
- Oliveira NC, Santos JL, Linhares MB. Audiovisual distraction for pain relief in paediatric inpatients: A crossover study. European Journal of Pain 2017;21(1):178-87. - PubMed
Pourmovahed 2013 {published data only}
Press 2003 {published data only}
-
- Press J, Gidron Y, Maimon M, Gonen A, Goldman V, Buskila D. Effects of active distraction on pain of children undergoing venipuncture: Who benefits from it? Pain Clinic 2003;15(3):261-9.
Ramírez‐Carrasco 2017 {published and unpublished data}
Rimon 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Rimon A, Shalom S, Wolyniez I, Gruber A, Schachter-Davidov A, Glatstein M. Medical clowns and cortisol levels in children undergoing venipuncture in the emergency department: A pilot study. Israel Medicine Association Journal 2016;18(11):680-3. - PubMed
Sahiner 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sahiner NC, Bal MD. The effects of three different distraction methods on pain and anxiety in children. Journal of Child Health Care 2016;20(3):277-85. - PubMed
Sander Wint 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sander Wint S, Eshelman D, Steele J, Guzzetta CE. Effects of distraction using virtual reality glasses during lumbar punctures in adolescents with cancer. ONF 2002;29(1):E8-15. - PubMed
Sinha 2006 {published data only}
-
- Sinha M, Christopher NC, Fenn R, Reeves L. Evaluation of nonpharmacologic methods of pain and anxiety management for laceration repair in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatrics 2006;117(4):1162-8. - PubMed
Tak 2006 {published data only}
-
- Tak JH, Van Bon WH. Pain- and distress-reducing interventions for venepuncture in children. Child: Care, Health, and Development 2006;32(3):257-68. - PubMed
Tyc 1997 {published data only}
-
- Tyc VL, Leigh L, Mulhern RK, Kumar Srivastava D, Bruce D. Evaluation of a cognitive-behavioral intervention for reducing distress in pediatric cancer patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging procedures. International Journal of Rehabilitation and Health 1997;3(4):267-79.
Vessey 1994 {published data only}
-
- Vessey JA, Carlson KL, McGill J. Use of distraction with children during an acute pain experience. Nursing Research 1994;43(6):369-72. - PubMed
Vosoghi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vosoghi N, Chehrzad M, Abotalebi G, Atrkar RZ. Effects of distraction on physiologic indices and pain intensity in children aged 3-6. Journal of Hayat 2010;16(3-4):39-47.
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang ZX, Sun LH, Chen AP. The efficacy of non-pharmacological methods of pain management in school age children receiving venepuncture in a paediatric department: a randomized controlled trial of audiovisual distraction and routine psychological intervention. Swiss Medical Weekly 2008;138(39-40):579-84. - PubMed
Windich‐Biermeier 2007 {published data only}
-
- Windich-Biermeier A, Sjoberg I, Dale JC, Eshelman D, Guzzetta CE. Effects of distraction on pain, fear, and distress during venous port access and venipuncture in children and adolescents with cancer. Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing 2007;24(1):8-19. - PubMed
Yinger 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yinger OS. Music therapy as procedural support for young children undergoing immunizations: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Music Therapy 2016;53(4):336-63. - PubMed
Zieger 2013 {published data only}
-
- Zieger B, Praskova M, Busse E, Barth M. A prospective randomised control study: reduction of children’s pain expectation using a picture book during blood withdrawal [Eine prospektive randomisierte Kontrollgruppenstudie: Reduktion kindlicher Schmerzerwartungen bei Blutentnahmen mithilfe eines Bilderbuches]. Klinische Padiatrie 2013;225(3):110-4. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agarwal 2008 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal A, Yadav G, Gupta D, Tandon M, Singh PK, Singh U. The role of a flash of light for attenuation of venous cannulation pain: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2008;106(3):814-6. - PubMed
Agarwal 2017 {published data only}
Alavi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Alavi A, Zargham A, Abdyzdan Z, Nmnbati M. The comparison of distraction and EMLA cream effects on pain intensity due to intravenous catheters in 5-12 years old thalassemic children. Journal of Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences 2005;7(3):9-15.
Alderfer 2010 {published data only}
Alhani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Alhani F. The effect of programmed distraction on the pain caused by venipuncture among adolescents on hemodialysis. Pain Management Nursing 2010;11(2):85-91. - PubMed
Anghelescu 2013 {published data only}
Anson 2010 {published data only}
-
- Anson L, Edmundson E, Teasley S. Implications of evidence-based venipuncture practice in a pediatric health care magnet facility. Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing 2010;41(4):179-85. - PubMed
Arts 1994 {published data only}
-
- Arts SE, Abu-Saad HH, Champion GD, Crawford MR, Fisher RJ, Juniper KH, et al. Age-related response to lidocaine-prilocaine (EMLA) emulsion and effect of music distraction on the pain of intravenous cannulation. Pediatrics 1994;93(5):797-801. - PubMed
Ashkenzai 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ashkenazi M, Blumer S, Eli I. Effectiveness of various modes of computerized delivery of local anesthesia in primary maxillary molars. Pediatric Dentistry 2006;28(1):29-39. - PubMed
Atkinson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Atkinson P, Chesters A, Heinz P. Pain management and sedation for children in the emergency department. BMJ 2009;339:b4234. - PubMed
Bagnasco 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bagnasco A, Pezzi E, Rosa F, Fornoni L, Sasso L. Distraction techniques in children during venipuncture: an Italian experience. Journal of Preventive Medicine and Hygiene 2012;53(1):44-8. - PubMed
Baxter 2011 {published data only}
-
- Baxter AL, Cohen LL, McElvery HL, Lawson ML, Von Baeyer CL. An integration of vibration and cold relieves venipuncture pain in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatric Emergency Care 2011;27(12):1151-6. - PubMed
Bengston 2002 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bengston BS, Jacobson RM, Friedrich WM, Vierkant RA, Poland GA. Teaching self-hypnosis to alleviate vaccination-related distress in children: a randomized, single-blinded controlled trial. In preparation.
Benjamin 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Benjamin AL, Hendrix TJ, Woody JL. Effects of vibration therapy in pediatric immunizations. Pediatric Nursing 2016;42(3):124-30. - PubMed
Ben‐Pazi 2017 {published data only}
Berberich 2009 {published data only}
-
- Berberich FR, Landman Z. Reducing immunization discomfort in 4- to 6-year-old children: A randomized clinical trial. Pediatrics 2009;124(2):e203-9. - PubMed
Berge 2017 {published data only}
-
- Berge KG, Agdal ML, Vika M, Skeie MS. Treatment of intra-oral injection phobia: a randomized delayed intervention controlled trial among Norwegian 10- to 16-year-olds. Acta Odontologica Scandinavica 2017;75(4):294–301. - PubMed
Boivin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Boivin JM, Poupon-Lemarquis L, Iraqi W, Fay R, Schmitt C, Rossignol P. A multifactorial strategy of pain management is associated with less pain in scheduled vaccination of children. A study realized by family practitioners in 239 children aged 4-12 years old. Family Practice 2008;25(6):423-9. - PubMed
Bowen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Bowen AM, Dammeyer MM. Reducing children's immunization distress in a primary care setting. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 1999;14(5):296-303. - PubMed
Broome 1998 {published data only}
-
- Broome ME, Rehwaldt M, Fogg L. Relationships between cognitive behavioral techniques, temperament, observed distress, and pain reports in children and adolescents during lumbar puncture. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 1998;13(1):48-54. - PubMed
Bruck 1995 {published data only}
-
- Bruck M, Ceci SJ, Francoeur E, Barr R. "I hardly cried when I got my shot!" Influencing children's reports about a visit to their pediatrician. Child Development 1995;66(1):193-208. - PubMed
Bufalini 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bufalini A. Role of interactive music in oncological pediatric patients undergoing painful procedures [Ruolo della musica interattiva nel paziente pediatrico oncologico sottoposto a procedure dolorose]. Minerva Pediatrica 2009;61(4):379-90. - PubMed
Bufalini 2012 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bufalini A. The effect of live music on oncological paediatric patients during painful procedures. European Journal of Integrative Medicine 2012.
Carlson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Carlson KL, Broome M, Vessey JA. Using distraction to reduce reported pain, fear, behavioral distress in children and adolescents: A multisite study. Journal of the Society of Pediatric Nurses 2000;5(2):75-85. - PubMed
Chan 2013 {published data only}
Chen 2000b {published data only}
-
- Chen E, Craske MG, Katz ER, Schwartz E, Zeltzer LK. Pain-sensitive temperament: Does it predict procedural distress and response to psychological treatment among children with cancer? Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2000;25(4):269-78. - PubMed
Chow 2017 {published data only}
-
- Chow CH, Van Lieshout RJ, Schmidt LA, Buckley N. Tablet-based intervention for reducing children’s preoperative anxiety: A pilot study. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 2017;38(6):409–16. - PubMed
Christiano 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Christiano BA. Children's coping and distress during invasive dental procedures: The effects of matching coping interventions to coping styles [Doctoral dissertation]. Case Western Reserve University, 1996.
Cline 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cline RJ, Harper FW, Penner LA, Peterson AM, Taub JW, Albrecht TL. Parent communication and child pain and distress during painful pediatric cancer treatments. Social Science & Medicine 2006;63(4):883-98. - PubMed
Cohen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Cohen LL, Blount RL, Panopoulos G. Nurse coaching and cartoon distraction: An effective and practical intervention to reduce child, parent, and nurse distress during immunizations. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1997;22(3):355-70. - PubMed
Cohen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cohen LL, Blount RL, Jansevics Cohen R, Ball CM, McClellan CB, Bernard RS. Children's expectations and memories of acute distress: Short- and long-term efficacy of pain management interventions. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2001;26(6):367-74. - PubMed
-
- Cohen LL, Blount RL, Jansevics Cohen R, Schaen ER, Zaff JF. Comparative study of distraction versus topical anesthesia for pediatric pain management during immunizations. Health Psychology 1999;18(6):591-8. - PubMed
Cohen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cohen LL, Bernard RS, Greco LA, McClellan CB. A child-focused intervention for coping with procedural pain: Are parent and nurse coaches necessary? Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2002;27(8):749-57. - PubMed
Cohen 2010 {published data only}
-
- Cohen L. A multifaceted distraction intervention may reduce pain and discomfort in children 4–6 years of age receiving immunisation. Evidence Based Nursing 2010;13(1):15-6. - PubMed
Cramer‐Berness 2005 {published data only}
-
- Cramer-Berness LJ, Friedman AG. Behavioral interventions for infant immunizations. Children's Health Care 2005;34(2):95-111.
Crowley 2011 {published data only}
-
- Crowley MA, Storer A, Heaton K, Naccarato MK, Proehl JA, Moretz JD, et al. Emergency nursing resource: needle-related procedural pain in pediatric patients in the emergency department. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2011;37(3):246-51. - PubMed
Cumino 2017 {published data only}
-
- Cumino DO, Vieira JE, Lima LC, Stievano LP, Silva RA, Mathias LA. Smartphone-based behavioural intervention alleviates children’s anxiety during anaesthesia induction. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2017;34(3):169–75. - PubMed
Dahlquist 2002 {published data only}
-
- Dahlquist LM, Pendley JS, Landthrip DS, Jones CL, Steuber CP. Distraction intervention for preschoolers undergoing intramuscular injections and subcutaneous port access. Health Psychology 2002;21(1):94-9. - PubMed
Dahlquist 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dahlquist LM, Shroff Pendley J. When distraction fails: Parental anxiety and children’s responses to distraction during cancer procedures. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2005;30(7):623-8. - PubMed
Davit 2011 {published data only}
Demir 2012 {published data only}
-
- Demir G, Cukurova Z, Eren G, Tekdos Y, Hergunsel O. The effect of "Multiphase Sedation" in the course of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging on children, parents and anesthesiologists. Revista Brasileira de Anestesiologia 2012;62(4):511-9. - PubMed
Drahota 2008 {published data only}
-
- Drahota A, Galloway E, Stores R, Ward D, Severs M, Dean T. Audiovisual distraction as an adjunct to pain and anxiety relief during minor surgery. Foot (Edinburgh) 2008;18(4):211-9. - PubMed
Dufresne 2010 {published data only}
-
- Dufresne A, Dugas MA, Samson Y, Barré P, Turcot L, Marc I. Do children undergoing cancer procedures under pharmacological sedation still report pain and anxiety? A preliminary study. Pain Medicine 2010;11(2):215-23. - PubMed
El‐Sharkawi 2012 {published data only}
-
- El-Sharkawi HF, El-Housseiny AA, Aly AM. Effectivness of new distraction technique on pain associated with injection of local anesthesia for children. Pediatric Dentistry 2012;34(2):142-5. - PubMed
Fancourt 2016 {published data only}
-
- Fancourt D, Lee C, Baltzer Nielsen S, Capps S, Brooks P. Relax anaesthetics: The effect of a bespoke distraction app on anxiety levels in children undergoing induction of anaesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2016;123(3S):292-3.
Fassler 1985 {published data only}
-
- Fassler D. The fear of needles in children. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1985;55(3):371-7. - PubMed
Felluga 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Felluga M, Rabach I, Minute M, Montico M, Giorgi R, Lonciari I, et al. A quasi randomized-controlled trial to evaluate the effectiveness of clowntherapy on children’s anxiety and pain levels in emergency department. European Journal of Pediatrics 2016;175(5):645–50. - PubMed
Firoozi 2014 {published data only}
-
- Firoozi M. Attention bias modification therapy (ABMT) as a modern technique for pain management in children with cancer. Pediatric Blood & Cancer 2014;61(S2):S250.
Forsner 2014 {published data only}
-
- Forsner M, Norstrom F, Nordyke K, Ivarsson A, Lindh V. Relaxation and guided imagery used with 12-year-olds during venipuncture in a school-based screening study. Journal of Child Health Care 2014;18(3):241-52. - PubMed
Franck 2014 {published data only}
-
- Franck LS, Berberich FR, Taddio A. Parent participation in a childhood immunization pain reduction method. Clinical Pediatrics 2014;54(3):228-35. - PubMed
Franzoi 2016 {published data only}
French 1994 {published data only}
-
- French GM, Painter EC, Coury DL. Blowing away shot pain: A technique for pain management during immunization. Pediatrics 1994;93(3):384-8. - PubMed
Garret‐Bernardin 2017 {published data only}
-
- Garret-Bernardin A, Cantile T, D’Antò V, Galanakis A, Fauxpoint G, Ferrazzano GF, et al. Pain experience and behavior management in pediatric dentistry: A comparison between traditional local anesthesia and the wand computerized delivery system. Pain Research & Management 2017;2017:7941238. - PMC - PubMed
Gilbert 1982 {published data only}
-
- Gilbert BO, Bennett Johnson S, Spillar R, McCallum M, Silverstein JH, Rosenbloom A. The effect of a peer-modelling film on children learning to self-inject insulin. Behavior Therapy 1982;13(2):186-93.
Goymour 2000 {published data only}
-
- Goymour K, Stephenson C, Goodenough B, Boulton C. Evaluating the role of play therapy in the pediatric emergency department. Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal 2000;3(2):10-2.
Hartling 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Hartling L, Newton AS, Liang Y, Jou H, Hewson K, Klassen TP, et al. Music to reduce pain and distress in the pediatric emergency department: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatrics 2013;167(9):826-35. - PubMed
Hatava 2000 {published data only}
-
- Hatava P, Olsson GL, Lagerkranser M. Preoperative psychological preparation for children undergoing ENT operations: a comparison of two methods. Paediatric Anaesthesia 2000;10(5):477-86. - PubMed
Hawkins 1998 {published data only}
-
- Hawkins PJ. Hypnosis in the alleviation of procedure related pain and distress in paediatric oncology patients. Contemporary Hypnosis 1998;15(4):199-207.
Heckler‐Medina 2006 {published data only}
-
- Heckler-Medina GA. The importance of child life and pain management during vascular access procedures in pediatrics. Journal of the Association for Vascular Access 2006;11(3):144-51.
Hedén 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hedén L, Von Essen L, Ljungman G. Randomized interventions for needle procedures in children with cancer. European Journal of Cancer Care 2009;18(4):358-63. - PubMed
Hillgrove‐Stuart 2013 {published data only}
Hoffman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Hoffmann F, Deanovic D. Prehospital pain management in children and adolescents [Präklinische Schmerztherapie bei Kindern und Jugendlichen]. Notfall and Rettungsmedizin 2011;14(7):549-53.
Howe 2011 {published data only}
-
- Howe CJ, Ratcliffe SJ, Tuttle A, Dougherty S, Lipman TH. Needle anxiety in children with type 1 diabetes and their mothers. MCN. American Journal of Maternal Child Nursing 2011;36(1):25-31. - PubMed
Hudson 2015 {published data only}
-
- Hudson BF, Ogden J, Whiteley MS. Randomized controlled trial to compare the effect of simple distraction interventions on pain and anxiety experienced during conscious surgery. European Journal of Pain 2015;19(10):1447-55. - PubMed
Inal 2010 {published data only}
-
- Inal S, Kelleci M. External thermomechanical stimulation and distraction are effective on pain relief of children during blood draw. In: 14th International Nursing Research Conference, Burgos. 2010.
Isong 2014 {published data only}
-
- Isong IA, Rao SR, Holifield C, Iannuzzi D, Hanson E, Ware J, et al. Addressing dental fear in children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A randomized controlled pilot study using electronic screen media. Clinical Pediatrics 2014;53(3):230–7. - PubMed
Jacobson 2006 {published data only}
-
- Jacobson AF. Cognitive-behavioral interventions for IV insertion pain. AORN Journal 2006;84(6):1031-48. - PubMed
Jay 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jay SM, Elliott CH, Katz E, Siegel SE. Cognitive-behavioral and pharmacologic interventions for children's distress during painful medical procedures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1987;55(6):860-5. - PubMed
Jay 1990 {published data only}
-
- Jay SM, Elliott CH. A stress inoculation program for parents whose children are undergoing painful medical procedures. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(6):799-804. - PubMed
Jay 1991 {published data only}
-
- Jay SM, Elliott CH, Woody PD. An investigation of cognitive-behavior therapy combined with oral Valium for children undergoing painful medical procedures. Health Psychology 1991;10(5):317-22. - PubMed
Jay 1995 {published data only}
-
- Jay S, Elliott CH, Fitzgibbons I, Woody P, Siegel S. A comparative study of cognitive behavior therapy versus general anesthesia for painful medical procedures in children. Pain 1995;62(1):3-9. - PubMed
Jibb 2017 {published data only}
-
- Jibb L, Stevens BJ, Nathan PC, Seto E, Cafazzo JA, Johnston DL, et al. Implementation and preliminary effectiveness of a real-time pain management smartphone app for adolescents with cancer: A multicenter pilot clinical study. Pediatric Blood & Cancer 2017;64(10):1-9. - PubMed
Jimeno 2014 {published data only}
-
- Jimeno FG, Mercade Bellido M, Cuadros Fernandez C, Lorente Rodriguez AI, Llopis Perez J, Boj Quesada JR. Effect of audiovisual distraction on children’s behaviour, anxiety and pain in the dental setting. European Journal of Paediatric Dentistry 2014;15(3):297-302. - PubMed
Kain 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kain ZN, Caldwell-Andrews AA, Mayes LC, Weinberg ME, Wang SM, MacLaren JE, et al. Family-centered preparation for surgery improves perioperative outcomes in children: a randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 2007;106(1):65-74. - PubMed
Kammerbauer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kammerbauer N, Becke K. Acute pain management in pediatric and geriatric medicine - pain measurement: What pain scale in which patients? [Akutschmerztherapie in pädiatrie und geriatrie - akutschmerztherapie im kindesalter]. Anästhesiologie, Intensivmedizin, Notfallmedizin, Schmerztherapie - AINS 2011;46:344-53. - PubMed
Kazak 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kazak AE, Penati B, Boyer BA, Himelstein B, Brophy P, Waibel MK, et al. A randomized controlled perspective outcome study of a psychological and pharmacological intervention protocol for procedural distress in pediatric leukemia. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1996;21(5):615-31. - PubMed
Kazak 1998 {published data only}
-
- Kazak AE, Penati B, Brophy P, Himelstein B. Pharmacologic and psychologic interventions for procedural pain. Pediatrics 1998;102(1):59-66. - PubMed
Kearl 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kearl YL, Yanger S, Montero S, Morelos-Howard E, Claudius I. Does combined use of the J-tip and Buzzy device decrease the pain of venipuncture in a pediatric population? Journal of Pediatric Nursing 2015;30(6):829–33. - PubMed
Kettwich 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kettwich SC, Sibbitt WL Jr, Brandt JR, Johnson CR, Wong CS, Bankhurst AD. Needle phobia and stress-reducing medical devices in pediatric and adult chemotherapy patients. Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing 2007;24(1):20-8. - PubMed
Klingman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Klingman A. Mass inoculation in a community: the effect of primary prevention of stress reactions. American Journal of Community Psychology 1985;13(3):323-32. - PubMed
Klorman 1980 {published data only}
-
- Klorman F, Hilpert PL, Michael R, LaGana C, Sveen OB. Effects of coping and mastery modelling on experienced and inexperienced pedodontic patients' disruptiveness. Behavior Therapy 1980;11(2):156-68.
Kolk 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kolk AM, Van Hoof R, Fiedeldij Dop MJC. Preparing children for venepuncture. The effect of an integrated intervention on distress before and during venipuncture. Child: Care, Health and Development 2000;26(3):251-60. - PubMed
Krauss 1996 {unpublished data only}
-
- Krauss WJ. Videotape modelling and parent participation: Effects on reducing distress behavior in children undergoing immunization procedures [Doctoral dissertation]. California School of Professional Psychology, 1996.
Kuttner 1988 {published data only}
-
- Kuttner L, Bowman M, Teasdale M. Psychological treatment of distress, pain, and anxiety for young children with cancer. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics 1988;9(6):374-81. - PubMed
Kwekkeboom 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Kwekkeboom KL. Music versus distraction for procedural pain and anxiety in patients with cancer. Oncology Nursing Forum 2003;30(3):433-40. - PubMed
Lawes 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lawes C, Sawyer L, Amos S, Kandiah M, Pearce L, Symons J. Impact of an education programme for staff working with children undergoing painful procedures. Paediatric Nursing 2008;20(2):33-7. - PubMed
Lee 2013 {published data only}
Lessi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lessi E, Biasutto M, Ferrazzo M. The pain from venipuncture in children: The benefit of visual distraction [Il dolore da venipuntura nel bambino: Il beneficio della distrazione con audiovisivi]. Gli Infermieri dei Bambini GISIP 2011;3(2):43-8.
Liossi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Liossi C, White P, Franck L, Hatira P. Parental pain expectancy as a mediator between child expected and experienced procedure-related pain intensity during painful medical procedures. Clinical Journal of Pain 2007;23(5):392-9. - PubMed
Lustman 1983 {published data only}
-
- Lustman NM. The effectiveness of two different components of stress inoculation, preparatory information and the teaching of coping devices aimed at mothers whose children are undergoing minor surgery [Doctoral dissertation]. Yale University, 1983.
MacLaren 2005 {published data only}
-
- MacLaren JE, Cohen LL. A comparison of distraction strategies for venipuncture distress in children. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2005;30(5):387-96. - PubMed
MacLaren 2007 {published data only}
Malone 1996 {published data only}
-
- Malone AB. The effects of live music on the distress of pediatric patients receiving intravenous starts, venipunctures, injections, and heel sticks. Journal of Music Therapy 1996;33(1):19-33.
Manimala 2000 {published data only}
-
- Manimala R, Blount RL, Cohen LL. The effects of parental reassurance versus distraction on child distress and coping during immunizations. Child Health Care 2000;29(3):161-77.
Manne 1990 {published data only}
-
- Manne SL, Redd WH, Jacobsen PB, Gorfinkle K, Schorr O. Behavioral intervention to reduce child and parent distress during venipuncture. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1990;58(5):565-72. - PubMed
Manne 1994 {published data only}
-
- Manne SL, Bakerman R, Jacobsen PB, Gorfinkle K, Redd WH. An analysis of a behavioral intervention for children undergoing venipuncture. Health Psychology 1994;13(6):556-66. - PubMed
Marec‐Bérard 2009 {published data only}
Marechal 2017 {published data only}
-
- Marechal C, Berthiller J, Tosetti S, Cogniat B, Desombres H, Bouvet L, et al. Children and parental anxiolysis in paediatric ambulatory surgery: a randomized controlled study comparing 0.3 mg kg-1 midazolam to tablet computer based interactive distraction. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2017;118(2):247–53. - PubMed
McCarthy 1998 {published data only}
-
- McCarthy AM, Cool VA, Hanrahan K. Cognitive behavioral interventions for children during painful procedures: research challenges and program development. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 1998;13(1):55-63. - PubMed
McCarthy 2014 {published data only}
McInally 2005 {published data only}
-
- McInally W. Whose line is it anyway? Management of central venous catheters in children. Paediatric Nursing 2005;17(5):14-8. - PubMed
McWhorter 2014 {published data only}
-
- McWhorter LG, Gil-Rivas V. The effect of brief functional relaxation on college students' needle anxiety during injected vaccinations. Journal of American College Health 2014;62(3):166-172. - PubMed
Megel 1998 {published data only}
-
- Megel ME, Houser CW, Gleaves LS. Children's responses to immunizations: Lullabies as a distraction. Issues in Comprehensive Pediatric Nursing 1998;21(3):129-45. - PubMed
Melamed 1974 {published data only}
-
- Melamed BG, Hawes RR, Heiby E, Glick J. Use of filmed modelling to reduce uncooperative behavior of children during dental treatment. Journal of Dental Research 1974;54(4):797-801. - PubMed
Moadad 2016 {published data only}
-
- Moadad N, Kozman K, Shahine R, Ohanian S, Badr LK. Distraction using the BUZZY for children during an IV insertion. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 2016;31(1):64–72. - PubMed
Mohan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Mohan S, Nayak R, Thomas RJ, Ravindran V. The effect of Entonox, play therapy and a combination on pain relief in children: a randomized controlled trial. Pain Management Nursing 2015;16(6):938-43. - PubMed
Mutlu 2015b {published data only}
-
- Mutlu B, Balcı S. Effects of balloon inflation and cough trick methods on easing pain in children during the drawing of venous blood samples: a randomized controlled trial. Journal for Specialists in Pediatric Nursing 2015;20(3):178-86. - PubMed
Myrvik 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Myrvik MP. A behavioral intervention targeting a reduction in child distress during a routine immunization [Dissertation]. University of North Dakota, 2008.
Nilsson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nilsson S, Finnström B, Kokinsky E, Enskär K. The use of Virtual Reality for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents in a paediatric oncology unit. European Journal of Oncology Nursing 2009;13(2):102-9. - PubMed
O'Laughlin 1995 {published data only}
-
- O'Laughlin E, Ridley-Johnson R. Maternal presence during children's routine immunizations: The effect of mother as observer in reducing child distress. Children's Health Care 1995;24(3):175-91. - PubMed
Oberoi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Oberoi J, Panda A, Garg I. Effect of hypnosis during administration of local anesthesia in six- to 16-year-old children. Pediatric Dentistry 2016;38(2):112-5. - PubMed
Olsen 1991 {published data only}
-
- Olsen BR. Brief interventions for routine use with children in a phlebotomy laboratory [Doctoral dissertation]. West Virginia University, 1991.
Ozdemir 2012 {published data only}
Park 2008 {published data only}
-
- Park SH, Bang SM, Nam E, Cho EK, Shin DB, Lee JH, et al. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of low-dose intravenous Lorazepam to reduce procedural pain during bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. Pain Medicine 2008;9(2):249-52. - PubMed
Pederson 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pederson C. Promoting parental use of nonpharmacologic techniques with children during lumbar punctures. Journal of Pediatric Oncology Nursing 1996;13(1):21-30. - PubMed
Peretz 1999 {published data only}
-
- Peretz B, Gluck GM. Assessing an active distracting technique for local anesthetic injection in pediatric dental patients: repeated deep breathing and blowing out air. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 1999;24(1):5-8. - PubMed
Posner 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Posner K. A pharmacobehavioral intervention to reduce child cancer distress [Doctoral dissertation]. Ferkauf Graduate School of Psychology, Yeshiva University, 1998.
Powers 1993 {published data only}
-
- Powers SW, Blount RL, Bachanas PJ, Cotter MW, Swan SC. Helping preschool leukemia patients and their parents cope during injections. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1993;18(6):681-95. - PubMed
Quan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Quan X, Joseph A, Nanda U, Moyano-Smith O, Kanakri S, Ancheta C, et al. Improving pediatric radiography patient stress, mood, and parental satisfaction through positive environmental distractions: a randomized control trial. Journal of Pediatric Nursing 2016;31(1):e11-e22. - PubMed
Rajan 2017 {published data only}
-
- Rajan D, Lakshman G, Gupta SK, Sivasubramanian R, Saxena A, Juneja R. Effect of recorded maternal voice on child’s cooperation during cardiac catheterization – A randomized controlled trial. Indian Pediatrics 2017;54(3):204-7. - PubMed
Ramponi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ramponi D. Reducing pain in pediatric procedures in the emergency department. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2009;35(4):379-82. - PubMed
Reeb 1997 {published data only}
-
- Reeb RN, Busch JP. Preprocedural psychological preparation in pediatric oncology: A process-oriented intervention study. Children's Health Care 1997;25(4):265-79.
Rogovik 2007 {published data only}
Russell 2012 {unpublished data only}
-
- Russell K, Nicholson R, Legge L, Leauanae E, Olsen A, Marsh S, et al. Reducing the pain of Bicillin injections in the rheumatic fever population of CMDHB. In: Journal of Paediatrics. Vol. 48. 2012:7.
Salih 2010 {published data only}
Santos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Santos LM, Borba RI, Sabates AL. The importance of the preschool in the preparation for intramuscular injection using the play [La importancia del preparo de ninos en edad prescolar para la injeccion intramuscular con el uso del juguete]. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem 2000;13(2):52-8.
Schechter 2010b {published data only}
-
- Schechter NL, Bernstein BA, Zempsky WT, Bright NS, Willard AK. Educational outreach to reduce immunization pain in office settings. Pediatrics 2010;126(6):1514-21. - PubMed
Schneider 2011 {published data only}
Schreiber 2016 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Schreiber S, Cozzi G, Rutigliano R, Assandro P, Tubaro M, Wiel LC, et al. Analgesia by cooling vibration during venipuncture in children with cognitive impairment. Acta Paediatrica 2016;105(1):e12–e16. - PubMed
Schur 1986 {unpublished data only}
-
- Schur JM. Alleviating behavioral distress with music or lamaze pant-blow breathing in children undergoing bone marrow aspirations and lumbar punctures [Doctoral dissertation]. The University of Texas Health Science Center at Dallas, 1986.
Seiden 2014 {published data only}
-
- Seiden SC, McMullan S, Sequera-Ramos L, De Oliveira GS Jr, Roth A, Rosenblatt A, et al. Tablet-based interaction distraction (TBID) vs oral midazolam to minimize preoperative anxiety in pediatric patients: a noninferiority randomized trial. Pediatric Anesthesia 2014;24(12):1217–23. - PubMed
Shabanloei 2010 {published data only}
-
- Shabanloei R, Golchin M, Esfahani A, Dolatkhah R, Rasoulian M. Effects of music therapy on pain and anxiety in patients undergoing bone marrow biopsy and aspiration. AORN Journal 2010;91(6):746-51. - PubMed
Shahabi 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shahabi M, Kalani-Tehrani D, Eghbal M, Alavi-Majd H, Abed Saidi J. Comparing the effects of EMLA ointment with a diversionary activity (music) on vein puncture pain at school-age children. Journal of Nursing and Midwifery 2007;17:56.
Shanmugam 2016 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Shanmugam RS, Subramani G. Effectiveness of distraction techniques upon pain among children receiving immunization. International Journal of Scientific Research 2016;5(2):517-20.
Shemesh 2017 {published data only}
-
- Shemesh E, D’Urso C, Knight C, Rubes M, Picerno KM, Posillico AM, et al. Food-allergic adolescents at risk for anaphylaxis: A randomized controlled study of supervised injection to improve comfort with epinephrine self-injection. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunolology: In Practice 2017;5(2):391-7. - PubMed
Shimizu 2005 {published data only}
-
- Shimizu T, Inomata S, Kihara S, Toyooka H, Brimacombe JR. Rapid injection reduces pain on injection with propofol. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2005;22(5):394-6. - PubMed
Sikorova 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sikorova L, Hrazdilova P. The effect of psychological intervention on perceived pain in children undergoing venipuncture. BioBiomedical Papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia 2011;155(2):149-54. - PubMed
Singh 2016 {published data only}
-
- Singh P. Effect of selected distraction techniques in behavior responses to pain among toddlers receiving invasive immunization. International Journal of Nursing and Medical Science 2016;5(1):504-12.
Skinner 2015 {published data only}
-
- Skinner SR, Davies C, Cooper S, Stoney T, Marshall H, Jones J, et al. Randomised controlled trial of a complex intervention to improve school-based HPV vaccination for adolescents: The HPV. EDU study. Sexually Transmitted Infections 2015;91:A77.
Slack 2009 {published data only}
Slifer 2009 {published data only}
Slifer 2011 {published data only}
-
- Slifer KJ, Hankinson JC, Zettler MA, Frutchey RA, Hendricks MC, Ward CM, et al. Distraction, exposure therapy, counterconditioning, and topical anesthetic for acute pain management during needle sticks in children with intellectual and developmental disabilities. Clinical Pediatrics 2011;50(8):688-97. - PubMed
Smith 1989 {published data only}
-
- Smith KE, Ackerson JD, Blotcky AD. Reducing distress during invasive medical procedures: Relating behavioral interventions to preferred coping style in pediatric cancer patients. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1989;14(3):405-19. - PubMed
Smith 1996 {published data only}
-
- Smith JT, Barabasz A, Barabasz M. Comparison of hypnosis and distraction in severely ill children undergoing painful medical procedures. Journal of Counseling Psychology 1996;43(2):187-95.
Sparks 2001 {published data only}
-
- Sparks L. Taking the "ouch" out of injections for children: Using distraction to decrease pain. American Journal of Maternal/Child Nursing 2001;26(2):72-8. - PubMed
Stefano 2005 {unpublished data only}
-
- Stefano C, Giancarlo I, Corrado V. The experience of control related to the procedure of non-pharmacologic pain management in paediatric oncology and heamatology. Poster abstract - no source identified. 2005.
Stevenson 2005 {published data only}
-
- Stevenson MD, Bivins CM, O'Brien K, Gonzalez del Rey JA. Child life intervention during angiocatheter insertion in the pediatric emergency department. Pediatric Emergency Care 2005;21(11):712-8. - PubMed
Suresh 2015 {published data only}
-
- Suresh BS, De Oliveira GS Jr, Suresh S. The effect of audio therapy to treat postoperative pain in children undergoing major surgery: A randomized controlled trial. Pediatric Surgery International 2015;31(2):197–201. - PubMed
Sury 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sury M, Bullock I, Rabar S, DeMott K. Sedation for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in children and young people: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ 2010;341:c6819. - PubMed
Thurgate 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thurgate C, Heppell S. Needle phobia--changing venepuncture practice in ambulatory care. Paediatric Nursing 2005;17(9):15-8. - PubMed
Tokunaga 2017 {published data only}
-
- Tokunaga N, Fukai K. Psychosomatic effects of blanketing in nursing care. Japan Journal of Nursing Science 2017;14(2):89–102. - PubMed
Tüfekci 2009 {published data only}
-
- Tüfekci FG, Celebioğlu A, Küçükoğlu S. Turkish children loved distraction: using kaleidoscope to reduce perceived pain during venipuncture. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2009;18(15):2180-6. - PubMed
Tyson 2014 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Tyson ME, Bohl DD, Blickman JG. A randomized controlled trial: child life services in pediatric imaging. Pediatric Radiology 2014;44(11):1426–32. - PubMed
Ujaoney 2013 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Ujaoney S, Mamtani M, Thakre T, Tote J, Hazarey V, Hazarey P, et al. Efficacy trial of Camouflage Syringe to reduce dental fear and anxiety. European Journal of Pediatric Dentistry 2013;14(4):273-8. - PubMed
Vernon 1974 {published data only}
-
- Vernon DT. Modeling and birth order in responses to painful stimuli. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 1974;29(6):794-9. - PubMed
Vika 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vika M, Skaret E, Raadal M, Ost LG, Kvale G. One- vs. five-session treatment of intra-oral injection phobia: a randomized clinical study. European Journal of Oral Sciences 2009;117(3):279-85. - PubMed
Vohra 2011 {published data only}
-
- Vohra S, Nilsson S. Does music therapy reduce pain and anxiety in children with cancer undergoing lumbar puncture? Focus on Alternative and Complementary Therapies 2011;16(1):66-7.
Wall 1989 {published data only}
-
- Wall VJ, Womack W. Hypnotic versus active cognitive strategies for alleviation of procedural distress in pediatric oncology patients. American Journal of Clinical Hypnosis 1989;31(3):181-91. - PubMed
Wallace 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wallace DP, Allen KD, Lacroix AE, Pitner SL. The "cough trick:" a brief strategy to manage pediatric pain from immunization injections. Pediatrics 2010;125(2):e367-73. - PubMed
Weber 2010 {published data only}
-
- Weber FS. The influence of playful activities on children's anxiety during the preoperative period at the outpatient surgical center. Jornal de Pediatria 2010;86(3):209-14. - PubMed
Weinstein 2003 {published data only}
-
- Weinstein P, Raadal M, Naidu S, Yoshida T, Kvale G, Milgrom P. A videotaped intervention to enhance child control and reduce anxiety of the pain of dental injections. European Journal of Paediatric Dentistry 2003;4(4):181-5. - PubMed
Winborn 1989 {published data only}
-
- Winborn MD. Associative and dissociative preparatory strategies for children undergoing dental treatment [Doctoral dissertation]. Memphis State University, 1989.
Wood 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wood C. Introducing a protocol for procedural pain. Paediatric Nursing 2002;14(8):30-3. - PubMed
Yoo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Yoo H, Kim S, Hur HK, Kim HS. The effects of an animation distraction intervention on pain response of preschool children during venipuncture. Applied Nursing Research 2011;24(2):94-100. - PubMed
Young 1988 {published data only}
-
- Young MR, Fu VR. Influence of play and temperament on the young child's response to pain. Children's Health Care 1988;16(3):209-15.
Zabin 1982 {unpublished data only}
-
- Zabin MA. The modification of children's behavior during blood work procedures [Doctoral dissertation]. West Virginia University, 1982.
Zahr 1998 {published data only}
-
- Zahr KL. Therapeutic play for hospitalized preschoolers in Lebanon. Pediatric Nursing 1998;24(5):449-54. - PubMed
Zeltzer 1982 {published data only}
-
- Zeltzer L, LeBaron S. Hypnosis and nonhypnotic techniques for reduction of pain and anxiety during painful procedures in children and adolescents with cancer. Pediatrics 1982;101(6):1032-5. - PubMed
Additional references
Accardi 2009
-
- Accardi MC, Milling LS. The effectiveness of hypnosis for reducing procedure-related pain in children and adolescents: A comprehensive methodological review. Journal of Behavior Medicine 2009;32:328-39. - PubMed
Altman 2001
-
- Altman DG, Schulz KF, Moher D, Egger M, Davidoff F, Elbourne D, et al, CONSORT GROUP (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials). The revised CONSORT statement for reporting randomized trials: Explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134:663-94. - PubMed
Alvarez 1997
-
- Alvarez CB, Marcos AF. Psychological treatment of evoked pain and anxiety by invasive medical procedures in paediatric oncology. Psychology in Spain 1997;1(1):17-36.
Andrews 2013a
-
- Andrews J, Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Alderson P, Dahm P, Falck-Ytter Y, et al. GRADE guidelines: 14. Going from evidence to recommendations: the significance and presentation of recommendations. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:719-25. - PubMed
Andrews 2013b
-
- Andrews J, Schunemann HJ, Oxman AD, Pottie K, Meerpohl J, Coello PA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 15. Going from evidence to recommendationddeterminants of a recommendation’s direction and strength. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:726-35. - PubMed
Barlow 1999
-
- Barlow DH, Durand VM. Abnormal Psychology: An Integrative Approach. California: Brooks/Cole Publishing Company, 1999.
Bauer 2015
Bellieni 2016
-
- Bellieni CV, Johnston CC. Analgesia, nil or placebo to babies, in trials that test new analgesic treatments for procedural pain. Acta Paediatrica 2016;105:129-36. - PubMed
Berberich 2012
-
- Berberich FR, Schechter NL. Pediatric office pain: crying for attention. Pediatrics 2012;129:e1057-59. - PubMed
Birnie 2014a
Birnie 2014b
Birnie 2015
-
- Birnie KA, Chambers CT, Taddio A, McMurtry CM, Noel M, Pillai Riddell R, et al HELPinKids&Adults Team. Psychological interventions for vaccine injections in children and adolescents: Systematic review of randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials. Clinical Journal of Pain 2015;31:S72-S89. - PMC - PubMed
Birnie 2017
-
- Birnie KA, Chambers CT, Spellman CM. Mechanisms of distraction in acute pain perception and modulation. Pain 2017;158:1012–1013. - PubMed
Blount 2003
-
- Blount RL, Piira T, Cohen LL. Management of pediatric pain and distress due to medical procedures. In: MC Roberts, editors(s). Handbook of Pediatric Psychology. 3rd edition. New York: The Guilford Press, 2003.
Boerner 2014
-
- Boerner KE, Gillespie JM, McLaughlin EN, Kuttner L, Chambers CT. Implementation of evidence-based psychological interventions for pediatric needle pain. Clinical Practice in Pediatric Psychology 2014;2:224–35.
Boerner 2015
-
- Boerner KE, Birnie KA, Chambers CT, Taddio A, McMurtry CM, Noel M, et al HELPinKids&Adults Team. Simple psychological interventions for reducing pain from common needle procedures in adults: Systematic review of randomized and quasi-randomized controlled trials. Clinical Journal of Pain 2015;31:S90–8. - PMC - PubMed
Broome 1990
-
- Broome ME, Bates TA, Lillis PP, McGahee TW. Children's medical fears, coping behaviors, and pain perceptions during a lumbar puncture. Oncology Nursing Forum 1990;17(3):361-7. - PubMed
Bukola 2017
-
- Bukola IM, Paula D. The effectiveness of distraction as procedural pain management technique in paediatric oncology patients: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2017;Epub ahead of print:Epub ahead of print. - PubMed
Caldwell 2012
-
- Caldwell PH, Dans L, De Vries MC, Newman J, Sammon H, Spriggs M, et al. Standard 1: Consent and recruitment. Pediatrics 2012;129:S118-23. - PubMed
Campbell 2017
-
- Campbell L, DiLorenzo M, Atkinson N, Pillai Riddell R. Systematic review: A systematic review of the interrelationships among children's coping responses, children's coping outcomes, and parent cognitive-affective, behavioral, and contextual variables in the needle-related procedures context. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2017;42:611-21. - PMC - PubMed
CDC 2018
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children and Adolescents Aged 18 Years or Younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/child-adolescent-complian... (accessed August 30, 2018).
Chambers 2009
-
- Chambers C, Taddio A, Uman L, McMurtry C. Psychological interventions for reducing pain and distress during routine childhood immunizations: a systematic review. Clinical Therapeutics 2009;31:S77-103. - PubMed
Chambers 2013
-
- Chambers CT, Taddio A, Stinson J, Campbell-Yeo M, Halperin S, Parker JA. It doesn't have to hurt: Strategies for helping children with shots and needles - A YouTube video for parents [Video file]. www.youtube.com/watch?v=KgBwVSYqfps (accessed 4 November 2013).
Chambers 2016
-
- Chambers CT, McMurtry CM, MacDonald N, Barwick M, Taddio A, Birnie K, et al. Needles Don't Have To Hurt. Parents Canada Advertorial all 2016.
Chen 2000a
-
- Chen E, Joseph MH, Zeltzer LK. Acute pain in children: Behavioral and cognitive interventions in the treatment of pain in children. Pediatric Clinics of North America 2000;47(3):1-13. - PubMed
Christophersen 2001
-
- Christophersen ER, Mortweet SL. Assessment and management of pain. In: Treatments that Work with Children: Empirically Supported Strategies for Managing Childhood Problems. Washington: American Psychological Association, 2001.
Cohen 1988
-
- Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences. 2nd edition. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., 1988.
Craig 2010
-
- Craig KD, Versloot J, Goubert L, Vervoort T, Crombez G. Perceiving pain in others: Automatic and controlled mechanisms. Journal of Pain 2010;11:101-108. - PubMed
Curran 2012
Flowers 2015
-
- Flowers SR, Birnie KA. Procedural preparation and support as a standard of care in pediatric oncology. Pediatric Blood and Cancer 2015;62:S668–73. - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT 2015 [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc.) GRADEpro GDT. Version Accessed 27 August 2018. Hamilton, ON: McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime, Inc.), 2015. Available from gradepro.org.
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:383-94. - PubMed
Guyatt 2013
-
- Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA, et al. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles-continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66:173-183. - PubMed
Hartling 2012
-
- Hartling L, Hamm M, Klassen T, Chen A-W, Meremikwu M, Moyer V, et al. Standard 2: Containing risk of bias. Pediatrics 2012;129:S124-31. - PubMed
Higgins 2017
-
- Higgins JPT, Churchill R, Chandler J, Cumpston MS (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017), Cochrane, 2017. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
IASP 2004
-
- IASP Task Force on Taxonomy. Classification of Chronic Pain. 2nd edition. Seattle: IASP Press, 2004.
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad A, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17:1-12. - PubMed
Jafari 2017
-
- Jafari H Courtois I, Van den Bergh O, Vlaeyen JWS, Van Diest I. Pain and respiration: A systematic review. Pain 2017;158:995-1006. - PubMed
Kazak 2001
-
- Kazak AE, Kunin-Batson A. Psychological and integrative interventions in pediatric procedure pain. In: GA Finley, PJ McGrath, editors(s). Acute and Procedure Pain in Infants and Children. Seattle: IASP Press, 2001:77-100.
Keefe 1992
-
- Keefe FJ, Dunsmore J, Burnett R. Behavioral and cognitive- behavioral approaches to chronic pain: Recent advances and future directions. Special issue: Behavioral medicine: An update for the 1990s. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1992;60(4):528-36. - PubMed
Kennedy 2008
-
- Kenney RM, Luhmann J, Zempsky WT. Clinical implications of unmanaged needle-insertion pain and distress in children. Pediatrics 2008;122:S130-3. - PubMed
Kenney 2016
-
- Kenney MP, Milling LS. The effectiveness of virtual reality distraction for reducing pain: A meta-analysis. Psychology of Consciousness: Theory, Research, and Practice 2016;3:199-210.
Klassen 2008
-
- Klassen J, Liang Y, Tjosvold L, Klassen T, Hartling L. Music for pain and anxiety in children undergoing medical procedures: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Acute Pain 2008;10(2):106. - PubMed
Ljungman 1999
-
- Ljungman G, Gordh T, Sorenson S, Kreuger A. Pain in paediatric oncology: interviews with children, adolescents and their parents. Acta Paediatrica 1999;88:623-30. - PubMed
McGrath 2008
-
- McGrath PJ, Walco GA, Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Brown MT, Davidson K, et al. Core outcome domains and measures for pediatric acute and chronic/recurrent pain clinical trials: PedIMMPACT recommendations. Journal of Pain 9;9:771-83. - PubMed
McMurtry 2015a
-
- McMurtry CM, Noel M, Taddio A, Antony MM, Asmundson GJ, Pillai Riddell R, et al HELPinKids&Adults Team. Interventions for individuals with high levels of needle fear: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials and quasi-randomized controlled trials. Clinical Journal of Pain 2015;31:S109-23. - PMC - PubMed
McMurtry 2015b
McMurtry 2016
-
- McMurtry CM, Taddio A, Noel M, Antony MM, Chambers CT, Asmundson GJ, et al. Exposure-based interventions for the management of individuals with high levels of needle fear across the lifespan: A clinical practice guideline and call for further research. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy 2016;45(3):217-35. - PMC - PubMed
MedLine 2004
-
- MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/mplusdictionary.html (accessed 4 February 2004).
Moher 2010
Morris 2011
NACI 2018
-
- National Advisory Committee on Immunization. Canada's Provincial and Territorial Routine (and Catch-up) Vaccination Routine Schedule Programs for Infants and Children, 2018. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/provincial-territorial-i... (accessed August 30, 2018).
Noel 2012
-
- Noel M, Chambers CT, Petter M, McGrath PJ, Klein RM, Stewart SH. "Pain is not over when the needle ends": A review and preliminary model of acute pain memory development in childhood. Pain Management 2012;2:487-97. - PubMed
Noel 2018
-
- Noel M, McMurtry CM, Pavlova M, Taddio A. Brief Clinical Report: A systematic review and meta-analysis of pain memory-reframining interventions for children's needle procedures. Pain Practice 2018;18(1):123-9. - PubMed
Pate 1996
-
- Pate JT, Blount RL, Cohen LL, Smith AJ. Childhood medical experience and temperament as predictors of adult functioning in medical situations. Children’s Health Care 1996;25:281-98.
Pillai‐Riddell 2011
Pillai‐Riddell 2015
Powers 1999
-
- Powers SW. Empirically supported treatments in pediatric psychology: Procedure-related pain. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 1999;24(2):131-45. - PubMed
Puntillo 2004
-
- Puntillo KA, Morris AB, Thompson CL, Stanik-Hutt J, White CA, Wild LR. Pain behaviors observed during six common procedures: Results from Thunder Project II. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32(2):421-7. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Richardson 2006
-
- Richardson J, Smith JE, McCall G, Pilkington K. Hypnosis for procedure-related pain and dis- tress in pediatric cancer patients: A systematic review of effectiveness and methodology related to hypnosis interventions. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 2006;31:70-84. - PubMed
Savovic 2012
-
- Savovic J, Jones HE, Altman DG, Harris RJ, Jüni P, Pildal J, et al. Influence of reported study design characteristics on intervention effect estimates from randomized, controlled trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2012;157:429-38. - PubMed
Schechter 2008
-
- Schechter NL. From the ouchless place to comfort central: The evolution of a concept. Pediatrics 2008;122:S154-60. - PubMed
Schechter 2010a
-
- Schechter NL, Finley GA, Bright NS, Laycock M, Forgeron P. ChildKind: A global initiative to reduce pain in children. Pediatric Pain Letter 2010;12:26-30.
Sinha 2012
-
- Sinha IP, Altman DG, Beresford MW, Boers M, Clarke M, Craig J, et al. Standard 5: Selection, measurements, and reporting of outcomes in clinical trials in children. Pediatrics 2012;129:S146-52. - PubMed
Skinner 2007
-
- Skinner EA, Zimmer-Gembeck MJ. The development of coping. Annual Review of Psychology 2007;58:119-44. - PubMed
Smith 2014
Stevens 2011
Stevens 2012
-
- Stevens BJ, Harrison D, Rashotte J, Yamada J, Abbott LK, Coburn G, et al. Pain assessment and intensity in hospitalized children in Canada. Journal of Pain 2012;13(9):857-65. - PubMed
Sucala 2013
Sweet 1998
-
- Sweet SD, McGrath PJ. Physiological measures of pain. In: GA Finley, PJ McGrath, editors(s). Measurement of Pain in Infants and Children. Seattle: IASP Press, 1998:59-81.
Taddio 2009
-
- Taddio A, Chambers CT, Halperin SA, Ipp M, Lockett D, Rieder, MJ, et al. Inadequate pain management during routine childhood immunizations: The nerve of it. Clinical Therapeutics 2009;31 Suppl 2:S152-67. - PubMed
Taddio 2012
-
- Taddio A, Ipp M, Thivakaran S, Jamal A, Parikh C, Smart S, et al. Survey of the prevalence of immunization non-compliance due to needle fears in children and adults. Vaccine 2012;30:4807-12. - PubMed
Taddio 2015
Uman 2008
-
- Uman LS, Chambers CT, McGrath PJ, Kisely S. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials examining psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents: An abbreviated Cochrane Review. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2008;33:842-54. - PMC - PubMed
Uman 2010
-
- Uman LS, Chambers CT, McGrath PJ, Kisely S, Matthews D, Hayton K. Assessing the quality of randomized controlled trials examining psychological interventions for pediatric procedural pain: Recommendations for quality improvement. Journal of Pediatric Psychology 2010;35:693-703. - PubMed
Van der Tweel 2012
-
- Van der Tweel I, Askie L, Vandermeer B, Ellenberg S, Fernandes RM, Saloojee H, et al. Standard 4: Determining adequate sample size. Pediatrics 2012;129:S138-45. - PubMed
Verhoeven 2012
-
- Verhoeven K, Goubert L, Jaaniste T, Van Ryckeghem DM, Crombez G. Pain catastrophizing influences the use and the effectiveness of distraction in schoolchildren. European Journal of Pain 2012;16:256-67. - PubMed
Von Baeyer 2017
-
- Von Baeyer CL, Jaaniste T, Vo HL, Brunsdon G, Lao H-C, Champion GD. Systematic review of self-report measures of pain intensity in 3- and 4-year-old children: Bridging a period of rapid cognitive development. Journal of Pain 2017;18:1017-26. - PubMed
WHO 2015
-
- World Health Organization. Meeting of the Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on immunization, April 2015: conclusions and recommendations. Weekly Epidemiological Record 29 May 2015;22:261-80.
WHO 2017
-
- World Health Organization. School-based Immunization. www.who.int/immunization/programmes_systems/policies_strategies/school_b... (accessed 23 March 2017).
WHO 2018
-
- World Health Organization. Table 1: Summary of WHO Position Papers - Recommendations for Routine Immunization, 2018. http://www.who.int/immunization/policy/Immunization_routine_table1.pdf (accessed August 30, 2018).
Williams 2012
-
- Williams K, Thomson D, Seto I, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Ioannidis JP, Curtis S, et al. Standard 6: Age groups for pediatric trials. Pediatrics 2012;129:S153-60. - PubMed
Wittmeier 2015
-
- Wittmeier KD, Klassen TP, Sibley KM. Implementation science in pediatric health care: Advances and opportunities. JAMA Pediatrics 2015;169:307-9. - PubMed
Young 2005
-
- Young KD. Pediatric procedural pain. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2005;45(2):160-71. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Uman 2005
Uman 2006
Uman 2013
-
- Uman LS, Birnie KA, Noel M, Parker JA, Chambers CT, McGrath PJ, Kisely SR. Psychological interventions for needle-related procedural pain and distress in children and adolescents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 10. Art. No: CD005179. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005179.pub3] - DOI - PubMed

