Detection of aquaporin-4 antibodies for patients with CNS inflammatory demyelinating diseases other than typical MS in Lithuania
- PMID: 30284401
- PMCID: PMC6236230
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1129
Detection of aquaporin-4 antibodies for patients with CNS inflammatory demyelinating diseases other than typical MS in Lithuania
Abstract
Objectives: Neuromyelitis optica (NMO) is frequently associated with aquaporin-4 autoantibodies (AQP4-Ab); however, studies of NMO in Lithuania are lacking. Therefore, the main objective of our study is to assess positivity for AQP4-Ab in patients presenting with inflammatory demyelinating central nervous system (CNS) diseases other than typical multiple sclerosis (MS) in Lithuania.
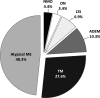
Materials and methods: Data were collected from the two largest University hospitals in Lithuania. During the study period, there were 121 newly diagnosed typical MS cases, which were included in the MS registry database. After excluding these typical MS cases, we analyzed the remaining 29 cases of other CNS inflammatory demyelinating diseases, including atypical MS (n = 14), acute transverse myelitis, TM (n = 8), acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, ADEM (n = 3), clinically isolated syndrome, CIS (n = 2), atypical optic neuritis, ON (n = 1), and NMO (n = 1). We assessed positivity for AQP4-Ab for the 29 patients and evaluated clinical, laboratory, and instrumental differences between AQP4-Ab seropositive and AQP4-Ab seronegative patient groups.
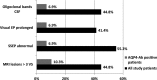
Results: AQP4-Ab test was positive for three (10.3%) patients in our study, with initial diagnoses of atypical MS (n = 2) and ADEM (n = 1). One study patient was AQP4-Ab negative despite being previously clinically diagnosed with NMO. There were no significant clinical, laboratory, or instrumental differences between the groups of AQP4-Ab positive (3 [10.3%]) and negative (26 [89.7%]) patients.
Conclusions: AQP4-Ab test was positive for one-tenth of patients with CNS inflammatory demyelinating diseases other than typical MS in our study. AQP4-Ab testing is highly recommended for patients presenting with not only TM and ON but also an atypical course of MS and ADEM.
Keywords: aquaporin-4 antibodies; neuromyelitis optica; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders.
© 2018 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Balnytė, R. (2012). Imunogenetinių veiksnių reikšmė sergančiųjų išsėtine skleroze ligos eigos formai ir negaliai [The role of immunogenetic factors on disease course and disability in multiple sclerosis]. PhD thesis. Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, Medical Academy, Kaunas.
-
- Bermel, R. A. , & Balcer, L. J. (2013). Optic neuritis and the evaluation of visual impairment in multiple sclerosis. Continuum (Minneap Minn), 19(4), 1074–1086. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan, E. P. , Weinshenker, B. G. , Krecke, K. N. , Lennon, V. A. , Lucchinetti, C. F. , McKeon, A. , … Pittock, S. J. (2015). Short myelitis lesions in aquaporin‐4‐IgG–positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders. JAMA Neurology, 72(1), 81–87. 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.2137 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jarius, S. , Franciotta, D. , Paul, F. , Ruprecht, K. , Bergamaschi, R. , Rommer, P. S. , … Wildemann, B. (2010). Cerebrospinal fluid antibodies to aquaporin‐4 in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders: Frequency, origin, and diagnostic relevance. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 7, 52 10.1186/1742-2094-7-52 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

