Critical Role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Asc1p in Translational Initiation at Elevated Temperatures
- PMID: 30285306
- PMCID: PMC6461043
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.201800208
Critical Role for Saccharomyces cerevisiae Asc1p in Translational Initiation at Elevated Temperatures
Abstract
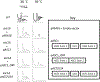
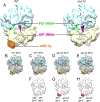
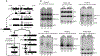
The eukaryotic ribosomal protein RACK1/Asc1p is localized to the mRNA exit channel of the 40S subunit but lacks a defined role in mRNA translation. Saccharomyces cerevisiae deficient in ASC1 exhibit temperature-sensitive growth. Using this null mutant, potential roles for Asc1p in translation and ribosome biogenesis are evaluated. At the restrictive temperature the asc1Δ null mutant has reduced polyribosomes. To test the role of Asc1p in ribosome stability, cryo-EM is used to examine the structure of 80S ribosomes in an asc1Δ yeast deletion mutant at both the permissive and nonpermissive temperatures. CryoEM indicates that loss of Asc1p does not severely disrupt formation of this complex structure. No defect is found in rRNA processing in the asc1Δ null mutant. A proteomic approach is applied to survey the effect of Asc1p loss on the global translation of yeast proteins. At the nonpermissive temperature, the asc1Δ mutant has reduced levels of ribosomal proteins and other factors critical for translation. Collectively, these results are consistent with recent observations suggesting that Asc1p is important for ribosome occupancy of short mRNAs. The results show the Asc1 ribosomal protein is critical in translation during heat stress.
Keywords: ASC1; initiation; ribosome; translation; yeast.
© 2018 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

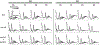
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

