Non-adherence to anti-tuberculosis treatment, reasons and associated factors among TB patients attending at Gondar town health centers, Northwest Ethiopia
- PMID: 30285907
- PMCID: PMC6167840
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-018-3789-4
Non-adherence to anti-tuberculosis treatment, reasons and associated factors among TB patients attending at Gondar town health centers, Northwest Ethiopia
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of non-adherence to anti-tuberculosis treatment, reasons and associated factors among TB patients attending at Gondar town health centers.
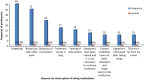
Result: A total of 314 participants were included with the response rate of 97.5%. The mean age of participants was 35.94 (SD ± 13.83) years. The overall rate of non-adherence to anti-TB treatment was 21.2% (95% CI 17.2, 26.1). Continuation phase of treatment (AOR = 2.27, 95% CI (1.54, 5.94)), presence of more than one co-morbidity (AOR = 6.22; 95% CI (2.21, 17.48)), poor knowledge about TB and anti-TB therapy (AOR = 4.11; 95% CI 1.57, 10.75), poor patient-provider relationship (AOR = 4.60, 95% CI 1.63, 12.97), and alcohol intake (AOR = 5.03; 95% CI 1.54, 16.40) were significantly associated with non-adherence. Forgetting 40 (23.1%), Being busy with other work 35 (20.2%), and being out of home/town 24 (13.9%) were the major reasons of participants for interruption of taking anti-TB medications.
Keywords: Ethiopia; Non-adherence; Prevalence; Reasons; Tuberculosis treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Organization WH . Global tuberculosis report 2017. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
-
- Organization WH. Multi drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) Uptodate WHO Global tuberculosis program; 2017.
-
- Organization WH . Global strategy and targets for tuberculosis prevention, care and control after 2015, the end TB strategy. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
-
- Schiffman G. Tuberculosis, Test, causes, treatment and Prognosis. eMedicineHealth. https://www.emedicinehealth.com/tuberculosis/article_em.htm.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases