Assessment and agreement of the CT appearance pattern and its severity grading of radiation-induced lung injury after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer
- PMID: 30286105
- PMCID: PMC6171841
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204734
Assessment and agreement of the CT appearance pattern and its severity grading of radiation-induced lung injury after stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Radiographic severity of radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) has not been well-studied. The goal of this study was to assess the CT appearance pattern and severity of RILI without consideration of the clinical presentation.
Material and methods: A total of 49 patients, 41 with primary lung cancer and 8 with metastatic lung cancer, were treated by 4-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT). RILI after SBRT was separately assessed by two observers. The early and late CT appearance patterns and CT-based severity grading were explored.
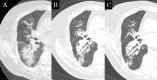
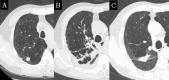
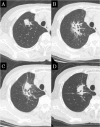
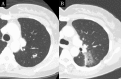
Results: The median follow-up period was 39.0 months. In the early CT findings of observers 1 and 2, there was diffuse consolidation in 15 and 8, diffuse ground glass opacity (GGO) in 0 and 0, patchy consolidation and GGO in 17 and 20, patchy GGO in 3 and 3, and no changes in 10 and 14, respectively (kappa = 0.61). In late CT findings of observer 1 and 2, there were modified conventional pattern in 28 and 24, mass-like pattern in 8 and 11, scar-like pattern in 12 and 12, and no changes in 1 and 2, respectively (kappa = 0.63). In the results of the CT-based grading by observers 1 and 2, there were grade 0 in 1 and 2, grade 1 in 10 and 14, grade 2 in 31 and 29, grade 3 in 7 and 4, and none of grade 4 or more, respectively (kappa = 0.66). According to multivariate analyses (MVA), the significant predicting factors of grade 2 or more CT-based RILI were age (p = 0.01), oxygen dependence (p = 0.03) and interstitial shadow (p = 0.03).
Conclusions: The agreement of the CT appearance and CT-based grading between two observers was good. These indicators may be able to provide us with more objective information and a better understanding of RILI.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CT patterns and serial CT Changes in lung Cancer patients post stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT).Cancer Imaging. 2022 Sep 16;22(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40644-022-00491-1. Cancer Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36114585 Free PMC article.
-
Early and late lung radiographic injury following stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT).Lung Cancer. 2010 Jul;69(1):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.09.006. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Lung Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19910075
-
The CT appearance pattern of radiation-induced lung injury and tumor recurrence after stereotactic body radiation therapy in early stage non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020 Jun;9(3):713-721. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-609. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32676333 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation injury of the lung after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for lung cancer: a timeline and pattern of CT changes.Eur J Radiol. 2011 Jul;79(1):147-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.10.029. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Eur J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 19954913 Review.
-
Lung abnormalities at multimodality imaging after radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer.Radiographics. 2011 May-Jun;31(3):771-89. doi: 10.1148/rg.313105096. Radiographics. 2011. PMID: 21571656 Review.
Cited by
-
High-dose thoracic radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a novel grading scale of radiation-induced lung injury for symptomatic radiation pneumonitis.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Jul 15;16(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01857-8. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34266462 Free PMC article.
-
A novel tool to evaluate and quantify radiation pneumonitis: A retrospective analysis of correlation of dosimetric parameters with volume of pneumonia patch.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 13;13:1130406. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1130406. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36994217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the relationship between the range of radiation-induced lung injury on CT images after IMRT for stage I lung cancer and dosimetric parameters.Ann Med. 2021 Dec;53(1):267-273. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2020.1869297. Ann Med. 2021. PMID: 33430616 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal analyses and predictive factors of radiation-induced lung toxicity-related parameters after stereotactic radiotherapy for lung cancer.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 2;17(12):e0278707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278707. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36459528 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of pre-existing interstitial lung disease on radiation and checkpoint inhibitor pneumonitis in lung cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025 May 9;17:17588359251338624. doi: 10.1177/17588359251338624. eCollection 2025. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40351325 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

