Application of insulin signaling to predict insect growth rate in Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)
- PMID: 30286156
- PMCID: PMC6171882
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204935
Application of insulin signaling to predict insect growth rate in Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae)
Abstract
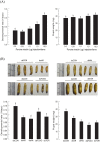
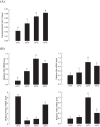
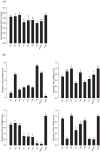
Insect growth is influenced by two major environmental factors: temperature and nutrient. These environmental factors are internally mediated by insulin/insulin-like growth factor signal (IIS) to coordinate tissue or organ growth. Maruca vitrata, a subtropical lepidopteran insect, migrates to different climate regions and feeds on various crops. The objective of this study was to determine molecular tools to predict growth rate of M. vitrata using IIS components. Four genes [insulin receptor (InR), Forkhead Box O (FOXO), Target of Rapamycin (TOR), and serine-threonine protein kinase (Akt)] were used to correlate their expression levels with larval growth rates under different environmental conditions. The functional association of IIS and larval growth was confirmed because RNA interference of these genes significantly decreased larval growth rate and pupal weight. Different rearing temperatures altered expression levels of these four IIS genes and changed their growth rate. Different nutrient conditions also significantly changed larval growth and altered expression levels of IIS components. Different local populations of M. vitrata exhibited significantly different larval growth rates under the same nutrient and temperature conditions along with different expression levels of IIS components. Under a constant temperature (25°C), larval growth rates showed significant correlations with IIS gene expression levels. Subsequent regression formulas of expression levels of four IIS components against larval growth rate were applied to predict growth patterns of M. vitrata larvae reared on different natural hosts and natural local populations reared on the same diet. All four formulas well predicted larval growth rates with some deviations. These results indicate that the IIS expression analysis explains the growth variation at the same temperature due to nutrient and genetic background.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insulin signaling mediates previtellogenic development and enhances juvenile hormone-mediated vitellogenesis in a lepidopteran insect, Maruca vitrata.BMC Dev Biol. 2019 Jul 5;19(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12861-019-0194-8. BMC Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31277577 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hemolymph trehalose titers by insulin signaling in the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae).Peptides. 2018 Aug;106:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Peptides. 2018. PMID: 29935203
-
Alteration of insulin signaling to control insect pest by using transformed bacteria expressing dsRNA.Pest Manag Sci. 2020 Mar;76(3):1020-1030. doi: 10.1002/ps.5612. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Pest Manag Sci. 2020. PMID: 31503391
-
Evolution and Function of the Insulin and Insulin-like Signaling Network in Ectothermic Reptiles: Some Answers and More Questions.Integr Comp Biol. 2016 Aug;56(2):171-84. doi: 10.1093/icb/icw046. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Integr Comp Biol. 2016. PMID: 27252221 Review.
-
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signalling (IIS) based regulation of lifespan across species.Biogerontology. 2017 Feb;18(1):35-53. doi: 10.1007/s10522-016-9670-8. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Biogerontology. 2017. PMID: 28101820 Review.
Cited by
-
Lactation in the human.Anim Front. 2023 Jun 14;13(3):64-70. doi: 10.1093/af/vfad021. eCollection 2023 Jun. Anim Front. 2023. PMID: 37324212 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Insulin signaling mediates previtellogenic development and enhances juvenile hormone-mediated vitellogenesis in a lepidopteran insect, Maruca vitrata.BMC Dev Biol. 2019 Jul 5;19(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12861-019-0194-8. BMC Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31277577 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous administration of dsRNA for the demonstration of RNAi in Maruca vitrata (lepidoptera: crambidae).3 Biotech. 2021 Apr;11(4):197. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02741-8. Epub 2021 Mar 27. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 33927988 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Alterations in Deletion Mutants of Two Insulin-Like Peptides Encoded in Maruca vitrata Using CRISPR/Cas9.Front Physiol. 2021 Jul 2;12:701616. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.701616. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34276424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nijhout HF. Development and evolution of adaptive polyphenisms. Evol Dev 2003;5:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Riddiford LM, Hiruma K, Zhou X, Nelson CA. Insights into the molecular basis of the hormonal control of molting and metamorphosis from Manduca sexta and Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2003;33:1327–1338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

