Biochemical significance of limonene and its metabolites: future prospects for designing and developing highly potent anticancer drugs
- PMID: 30287506
- PMCID: PMC6239267
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20181253
Biochemical significance of limonene and its metabolites: future prospects for designing and developing highly potent anticancer drugs
Abstract
Monocyclic monoterpenes have been recognized as useful pharmacological ingredients due to their ability to treat numerous diseases. Limonene and perillyl alcohol as well as their metabolites (especially perillic acid and its methyl ester) possess bioactivities such as antitumor, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial agents. These therapeutic properties have been well documented. Based on the aforementioned biological properties of limonene and its metabolites, their structural modification and development into effective drugs could be rewarding. However, utilization of these monocyclic monoterpenes as scaffolds for the design and developments of more effective chemoprotective agents has not received the needed attention by medicinal scientists. Recently, some derivatives of limonene metabolites have been synthesized. Nonetheless, there have been no thorough studies on their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties as well as their inhibition against isoprenylation enzymes. In this review, recent research progress in the biochemical significance of limonene and its metabolites was summarized with emphasis on their antitumor effects. Future prospects of these bioactive monoterpenes for drug design and development are also highlighted.
Keywords: limonene; metabolites; monoterpenes; pharmacological.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


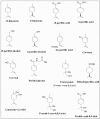
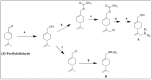
References
-
- Simonsen J.L., Owen L.N., Barton D.H.R. and Ross W.C.J. (1947) The Terpenes, University Press, Cambridge
-
- Sun J. (2007) d-Limonene safety and clinical applications. Altern. Med. Rev. 12, 259 - PubMed
-
- Fujita T. and Nakayama M. (1993) Monoterpene glucosides and other constituents from Perilla frutescens. Phytochemistry 34, 1545–1548 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)90843-4 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

