Mosaicism and incomplete penetrance of PCDH19 mutations
- PMID: 30287595
- PMCID: PMC6581080
- DOI: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-105235
Mosaicism and incomplete penetrance of PCDH19 mutations
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the PCDH19 gene have mainly been reported in female patients with epilepsy. To date, PCDH19 mutations have been reported in hundreds of females and only in 10 mosaic male epileptic patients with mosaicism.
Objective: We aimed to investigate the occurrence of mosaic PCDH19 mutations in 42 families comprising at least one patient with PCDH19-related epilepsy.
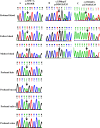
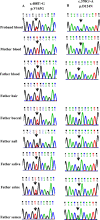
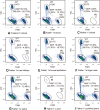
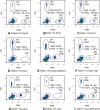
Methods: Two male patients with mosaic PCDH19 variants were identified using targeted next-generation sequencing. Forty female patients with PCDH19 variants were identified by Sanger sequencing and Multiple Ligation Probe Amplification (MLPA). Microdroplet digital PCR was used to quantify the mutant allelic fractions (MAFs) in 20 families with PCDH19 variants.
Results: Five mosaic individuals, four males and one female, were identified in total. Mosaic variant was confirmed in multiple somatic tissues from one male patient and in blood from the other male patient. Among 22 female patients harbouring a newly occurred PCDH19 variant identified by Sanger sequencing and MLPA, Sanger sequencing revealed two mosaic fathers (9%, 2/22), one with two affected daughters and the other with an affected child. Two asymptomatic mosaic fathers were confirmed as gonosomal mosaicism, with MAFs ranging from 4.16% to 37.38% and from 1.27% to 19.13%, respectively. In 11 families with apparent de novo variants, 1 female patient was identified as a mosaic with a blood MAF of 26.72%.
Conclusion: Our study provides new insights into phenotype-genotype correlations in PCDH19 related epilepsy and the finding of high-frequency mosaicism has important implications for genetic counselling.
Keywords: epilepsy; mddpcr; mosaicism; pcdh19; sequencing.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NGS-Based Identification of Two Novel PCDH19 Mutations in Female Patients with Early-Onset Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 24;25(11):5732. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115732. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891919 Free PMC article.
-
PCDH19 Pathogenic Variants in Males: Expanding the Phenotypic Spectrum.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1298:177-187. doi: 10.1007/5584_2020_574. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32852734
-
PCDH19-related epileptic encephalopathy in a male mosaic for a truncating variant.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Jun;170(6):1585-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37617. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 27016041
-
PCDH19-related infantile epileptic encephalopathy: an unusual X-linked inheritance disorder.Hum Mutat. 2012 Apr;33(4):627-34. doi: 10.1002/humu.22029. Epub 2012 Feb 14. Hum Mutat. 2012. PMID: 22267240 Review.
-
Disentangling the paradox of the PCDH19 clustering epilepsy, a disorder of cellular mosaics.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Dec;65:169-175. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.06.012. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32726744 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of seizure susceptibility in Pcdh19 mice.Epilepsia. 2020 Oct;61(10):2313-2320. doi: 10.1111/epi.16675. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Epilepsia. 2020. PMID: 32944953 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic characteristics and prenatal diagnosis of patients presented GDD/ID with rare monogenic causes.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Nov 11;15(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01599-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 33176815 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Very Low-Level Somatic Mosaic COL4A5 Splicing Variant in Asymptomatic Female Using Droplet Digital PCR.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 7;9:847056. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.847056. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35360741 Free PMC article.
-
ATP1A3 mosaicism in families with alternating hemiplegia of childhood.Clin Genet. 2019 Jul;96(1):43-52. doi: 10.1111/cge.13539. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Clin Genet. 2019. PMID: 30891744 Free PMC article.
-
The role of somatic mutational events in the pathogenesis of epilepsy.Curr Opin Neurol. 2019 Apr;32(2):191-197. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000667. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30762606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dibbens LM, Tarpey PS, Hynes K, Bayly MA, Scheffer IE, Smith R, Bomar J, Sutton E, Vandeleur L, Shoubridge C, Edkins S, Turner SJ, Stevens C, O’Meara S, Tofts C, Barthorpe S, Buck G, Cole J, Halliday K, Jones D, Lee R, Madison M, Mironenko T, Varian J, West S, Widaa S, Wray P, Teague J, Dicks E, Butler A, Menzies A, Jenkinson A, Shepherd R, Gusella JF, Afawi Z, Mazarib A, Neufeld MY, Kivity S, Lev D, Lerman-Sagie T, Korczyn AD, Derry CP, Sutherland GR, Friend K, Shaw M, Corbett M, Kim HG, Geschwind DH, Thomas P, Haan E, Ryan S, McKee S, Berkovic SF, Futreal PA, Stratton MR, Mulley JC, Gécz J. X-linked protocadherin 19 mutations cause female-limited epilepsy and cognitive impairment. Nat Genet 2008;40:776–81. 10.1038/ng.149 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Depienne C, Trouillard O, Bouteiller D, Gourfinkel-An I, Poirier K, Rivier F, Berquin P, Nabbout R, Chaigne D, Steschenko D, Gautier A, Hoffman-Zacharska D, Lannuzel A, Lackmy-Port-Lis M, Maurey H, Dusser A, Bru M, Gilbert-Dussardier B, Roubertie A, Kaminska A, Whalen S, Mignot C, Baulac S, Lesca G, Arzimanoglou A, LeGuern E. Mutations and deletions in PCDH19 account for various familial or isolated epilepsies in females. Hum Mutat 2011;32:E1959–E1975. 10.1002/humu.21373 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Harssel JJ, Weckhuysen S, van Kempen MJ, Hardies K, Verbeek NE, de Kovel CG, Gunning WB, van Daalen E, de Jonge MV, Jansen AC, Vermeulen RJ, Arts WF, Verhelst H, Fogarasi A, de Rijk-van Andel JF, Kelemen A, Lindhout D, De Jonghe P, Koeleman BP, Suls A, Brilstra EH. Clinical and genetic aspects of PCDH19-related epilepsy syndromes and the possible role of PCDH19 mutations in males with autism spectrum disorders. Neurogenetics 2013;14:23–34. 10.1007/s10048-013-0353-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Depienne C, Bouteiller D, Keren B, Cheuret E, Poirier K, Trouillard O, Benyahia B, Quelin C, Carpentier W, Julia S, Afenjar A, Gautier A, Rivier F, Meyer S, Berquin P, Hélias M, Py I, Rivera S, Bahi-Buisson N, Gourfinkel-An I, Cazeneuve C, Ruberg M, Brice A, Nabbout R, Leguern E. Sporadic infantile epileptic encephalopathy caused by mutations in PCDH19 resembles Dravet syndrome but mainly affects females. PLoS Genet 2009;5:e1000381 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000381 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
