ER stress signaling has an activating transcription factor 6α (ATF6)-dependent "off-switch"
- PMID: 30287689
- PMCID: PMC6254332
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002121
ER stress signaling has an activating transcription factor 6α (ATF6)-dependent "off-switch"
Abstract
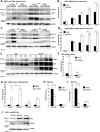
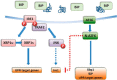
In response to an accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumen, three ER transmembrane signaling proteins, inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), PRKR-like ER kinase (PERK), and activating transcription factor 6α (ATF6α), are activated. These proteins initiate a signaling and transcriptional network termed the unfolded protein response (UPR), which re-establishes cellular proteostasis. When this restoration fails, however, cells undergo apoptosis. To investigate cross-talk between these different UPR enzymes, here we developed a high-content live cell screening platform to image fluorescent UPR-reporter cell lines derived from human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells in which different ER stress signaling proteins were silenced through lentivirus-delivered shRNA constructs. We observed that loss of ATF6 expression results in uncontrolled IRE1-reporter activity and increases X box-binding protein 1 (XBP1) splicing. Transient increases in both IRE1 mRNA and IRE1 protein levels were observed in response to ER stress, suggesting that IRE1 up-regulation is a general feature of ER stress signaling and was further increased in cells lacking ATF6 expression. Moreover, overexpression of the transcriptionally active N-terminal domain of ATF6 reversed the increases in IRE1 levels. Furthermore, inhibition of IRE1 kinase activity or of downstream JNK activity prevented an increase in IRE1 levels during ER stress, suggesting that IRE1 transcription is regulated through a positive feed-forward loop. Collectively, our results indicate that from the moment of activation, IRE1 signaling during ER stress has an ATF6-dependent "off-switch."
Keywords: APY29; ATF6; GRP78; IRE1; UPR reporters; X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1); c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK); cell death; endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress); fluorescent reporter; high content imaging; imaging; lentivirus; protein misfolding; stress response; unfolded protein response (UPR).
© 2018 Walter et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures






Similar articles
-
Imaging of single cell responses to ER stress indicates that the relative dynamics of IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/ATF4 signalling rather than a switch between signalling branches determine cell survival.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Sep;22(9):1502-16. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.241. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25633195 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional induction of the human asparagine synthetase gene during the unfolded protein response does not require the ATF6 and IRE1/XBP1 arms of the pathway.Biochem J. 2009 Feb 1;417(3):695-703. doi: 10.1042/BJ20081706. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 18840095 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress by the anti-cancer agent, di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT): Activation of PERK/eIF2α, IRE1α, ATF6 and calmodulin kinase.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 1;109:27-47. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27059255
-
Molecular signal networks and regulating mechanisms of the unfolded protein response.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Jan.;18(1):1-14. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600043. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 28070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The molecular mechanism and functional diversity of UPR signaling sensor IRE1.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 15;265:118740. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118740. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33188833 Review.
Cited by
-
The roles and mechanisms of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy in animal viral infections.Vet Res. 2024 Sep 3;55(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01360-4. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39227990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordinated signaling of activating transcription factor 6α and inositol-requiring enzyme 1α regulates hepatic stellate cell-mediated fibrogenesis in mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):G864-G879. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00453.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33728997 Free PMC article.
-
Increased cellular protein modification by methylglyoxal activates endoplasmic reticulum-based sensors of the unfolded protein response.Redox Biol. 2024 Feb;69:103025. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103025. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38199038 Free PMC article.
-
Giardia duodenalis-induced G0/G1 intestinal epithelial cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involve activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress in vitro.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 15;14:1127552. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1127552. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006313 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved wobble uridine tRNA thiolase Ctu1 is required for angiogenesis and embryonic development.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 20;19(12):e0315854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315854. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39705244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han J., Back S. H., Hur J., Lin Y. H., Gildersleeve R., Shan J., Yuan C. L., Krokowski D., Wang S., Hatzoglou M., Kilberg M. S., Sartor M. A., and Kaufman R. J. (2013) ER stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 481–490 10.1038/ncb2738 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shoulders M. D., Ryno L. M., Genereux J. C., Moresco J. J., Tu P. G., Wu C., Yates J. R. 3rd., Su A. I., Kelly J. W., and Wiseman R. L. (2013) Stress-independent activation of XBP1s and/or ATF6 reveals three functionally diverse ER proteostasis environments. Cell Rep. 3, 1279–1292 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

