Oncologic and Cosmetic Outcomes of Oncoplastic Breast Surgery in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Experience from a Developing Country
- PMID: 30287987
- PMCID: PMC6154377
- DOI: 10.1007/s13193-017-0689-3
Oncologic and Cosmetic Outcomes of Oncoplastic Breast Surgery in Locally Advanced Breast Cancer After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Experience from a Developing Country
Abstract
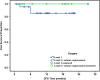
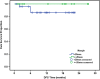
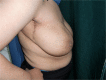
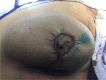
Oncoplastic surgery (OPS) has emerged as a new approach for extending breast conserving surgery (BCS) possibilities, reducing both mastectomy and re-excision rates, while avoiding breast deformities. OPS is based upon the integration of plastic surgery techniques for immediate reshaping after wide excision for breast cancer. This is a prospective feasibility cohort study of oncoplastic breast surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy that was carried at the National Cancer Institute, Cairo University and included 70 patients. The primary outcome was the local recurrence rate. Secondary outcomes included survival and margins obtained as well as cosmetic outcomes. Survival analysis was performed. Oncoplastic breast surgery did not compromise oncologic safety in the patients included in the study. It even allowed wider margins of resection which could be associated with better oncologic outcomes. At the same time, it gave a better cosmetic outcome and therefore higher patient satisfaction. Oncoplastic breast surgery includes a wide spectrum of surgical techniques, ranging from the basic level I techniques in breast conserving surgery to the more complex procedures of level II which are broadly classified into volume replacement (therapeutic mammoplasty) and volume displacement procedures. We suggest that oncoplastic breast surgery techniques should be the standard of care in breast surgery. They are the basis for breast conserving surgery techniques in early breast cancer. In our experience, oncoplastic surgery is feasible in locally advanced tumours after downstaging with neoadjuvant chemotherapy without compromising the oncologic safety.
Keywords: Breast; Egypt; Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy; Oncoplastic Surgery; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there is no conflict of interest in this article.Ethical approval was obtained by the Ethics Committee at the National Cancer Institute, Cairo University, April 2011.
Figures




References
-
- AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) (2002) Cancer staging manual, 6th ed. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, et al (Eds), Springer-Verlag, New York. p. 223
-
- American College of Radiology (2003) Breast imaging reporting and data systems (BI-RADS). American College of Radiology, Reston, VA
-
- Curran D, van Dongen JP, Aaronson NK, et al. Quality of life of early-stage breast cancer patients treated with radical mastectomy or breast-conserving procedures: results of EORTC Trial 10801. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC), Breast Cancer Cooperative Group (BCCG) Eur J Cancer. 1998;34:307. doi: 10.1016/S0959-8049(97)00312-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
