Effects of oral probiotic supplementation on gut Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium populations and the clinical status of low-birth-weight preterm neonates: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 30288066
- PMCID: PMC6160268
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S166348
Effects of oral probiotic supplementation on gut Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium populations and the clinical status of low-birth-weight preterm neonates: a multicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Aim: Probiotic bacteria administered directly after birth to preterm neonates may improve gastrointestinal function and may reduce the incidence of late-onset sepsis, which is a frequent complication in this group.
Purpose: The main objective of this study was to evaluate whether a new probiotic bacterial mixture of Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL53A and Bifidobacterium breve PB04 given to preterm, low-birth-weight neonates would influence composition of their gut microbiota and sepsis rates.
Patients and methods: This study was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in clinical centers of neonatal care in Poland. A probiotic or placebo preparation was given twice daily to 181 preterm low-birth-weight neonates who were eligible for enteral feeding between July 2012 and July 2013. The probiotic was given to 90 neonates, while placebo was given to 91 neonates. The gut microbiota was monitored by microbiological analysis of stool samples. Sepsis episodes were detected on the basis of clinical and laboratory findings and confirmed by blood cultures.
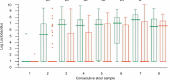
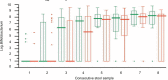
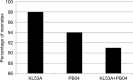
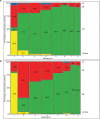
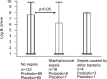
Results: Tested probiotic administration resulted in continuous increase of the Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium counts in the gut microbiota. The applied tested strains successfully colonized the neonates gut since they were present in over 90% of stool samples, which was confirmed by molecular analysis. Regardless of the study group (probiotic or placebo), B. breve colonization correlated with lower staphylococcal sepsis incidence, which was irrespective of whether probiotics were given. No sepsis case caused by strains included in study probiotic was recorded.
Conclusion: Appropriately selected and characterized probiotic bacteria may be safely given to preterm neonates to normalize their distorted gut microbiota and may contribute to lower staphylococcal sepsis rates.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium; LBW neonates; Lactobacillus; gut microbiota; probiotics; staphylococcal sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Rønnestad A, Abrahamsen TG, Medbø S, et al. Sepicemia in the first week of life in a Norwegian national cohort of extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 2005;115(3):e262–e268. - PubMed
-
- Cherifi S, Byl B, Deplano A, et al. Genetic characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from patients with catheter-related bloodstream infections and from colonized health-care workers in a Belgian hospital. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2014;13:20. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maki DG, Weise CE, Sarafin HW. A semiquantitative culture method for identifying intravenous-catheter-related infection. N Engl J Med. 1977;296(23):1305–1309. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

