Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives
- PMID: 30288073
- PMCID: PMC6163009
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S146339
Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: current perspectives
Abstract
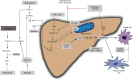
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is rapidly becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease due to an increase in the prevalence of obesity. The development of NASH leads to an increase in morbidity and mortality. While the first line of treatment is lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and increased physical activity, there are no approved pharmacological treatment agents for NAFLD and NASH currently. Due to its complex pathophysiology, different pathways are under investigation for drug development with the focus on metabolic pathways, inflammation, and slowing or reversing fibrosis. There are several agents advancing in clinical trials, and promising results have been seen with drugs that affect hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. This review will provide an overview on NAFLD and some of the mechanisms of disease that are being targeted with pharmacologic agents.
Keywords: antifibrotics; clinical trials; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; pharmacotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Onyekwere CA, Ogbera AO, Samaila AA, Balogun BO, Abdulkareem FB. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Synopsis of current developments. Niger J Clin Pract. 2015;18(6):703–712. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328–357. - PubMed
-
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41(6):1313–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

